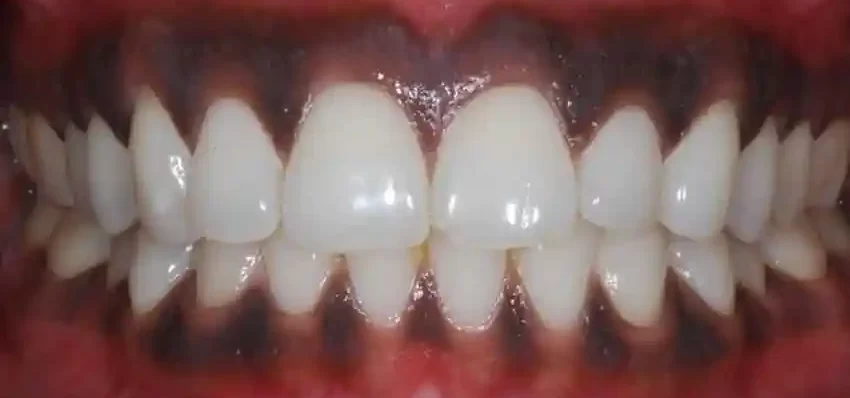
Oral health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being, and any unusual changes in the mouth can be concerning. One such change that individuals may notice is the discoloration of the gums, specifically the development of black or darkened gums. While most people are familiar with the typical pink appearance of healthy gums, black gums can be a cause for worry and warrant further investigation. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, potential complications, and available treatments for black gums.
Table of Contents
ToggleCauses of Black Gums
- Melanin Deposits
- Ethnic Background
- Smoking and Tobacco Use
- Oral Hygiene Habits
- Medications
- Medical Conditions
- Hormonal Changes
- Dental Restorations
Melanin Deposits
One of the primary reasons for the development of black gums is an increased deposition of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color. Melanin levels can vary among individuals, and some people may naturally have higher concentrations of melanin in their gums, leading to a darker appearance.
Ethnic Background
Genetic factors play a significant role in the color of an individual’s gums. People with African, Asian, or Indigenous backgrounds are more likely to have naturally darker gums due to higher melanin levels.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Tobacco products, especially cigarettes, contain harmful chemicals that can lead to gum discoloration. Regular tobacco use can restrict blood flow to the gums, causing them to darken over time.
Oral Hygiene Habits
Poor oral hygiene can contribute to the buildup of plaque and tartar on the gums, which can lead to gum inflammation and discoloration. Inadequate brushing and flossing allow bacteria to thrive, causing the gums to appear darker.
Medications
Some medications, such as certain antimalarial drugs, can lead to hyperpigmentation of the gums as a side effect. It’s essential to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as Addison’s disease and Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, can cause darkening of the gums. These conditions are relatively rare but can have oral manifestations.
Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy and hormonal changes can affect melanin production, potentially leading to gum discoloration.
Dental Restorations
Improperly placed dental restorations, such as crowns or fillings, can cause the gums to react and become discolored over time.
Symptoms of Black Gums
- Color Change
- Gum Sensitivity
- Bleeding
- Halitosis (Bad Breath)
Color Change
The most noticeable symptom of black gums is a change in the color of the gums, ranging from light brown to deep black.
Gum Sensitivity
Discolored gums may also be accompanied by increased sensitivity, discomfort, or tenderness.
Bleeding
Darkened gums may bleed more easily during brushing or flossing, indicating potential gum inflammation or periodontal disease.
Halitosis (Bad Breath)
Poor oral hygiene associated with black gums can lead to bad breath, which can negatively impact social interactions and self-confidence.
Complications and Risks
Ignoring black gums could potentially lead to more severe oral health issues, such as:
- Gingivitis
- Periodontitis
- Oral Infections
- Psychosocial Impact
Gingivitis
Darkened gums can be a sign of gingivitis, an early stage of gum disease characterized by inflammation and bleeding gums.
Periodontitis
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more advanced form of gum disease that can lead to gum recession, tooth mobility, and even tooth loss.
Oral Infections
Discolored gums may be more prone to infections, causing discomfort and affecting overall oral health.
Psychosocial Impact
Darkened gums can negatively affect an individual’s self-esteem and confidence, leading to social and psychological challenges.
Treatment Options
- Improved Oral Hygiene
- Professional Dental Cleaning
- Smoking Cessation
- Medication Review
- Gum Depigmentation
- Addressing Underlying Conditions
Improved Oral Hygiene
Practicing good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and routine dental check-ups, can help prevent and manage gum discoloration.
Professional Dental Cleaning
A dental professional can perform a thorough cleaning to remove plaque, tartar, and stains that contribute to gum discoloration.
Smoking Cessation
Quitting tobacco use can not only improve gum health but also prevent further discoloration and potential complications.
Medication Review
If gum discoloration is a side effect of a medication, consult a healthcare provider to explore alternative treatment options.
Gum Depigmentation
For individuals seeking a cosmetic solution, gum depigmentation procedures can be performed to lighten the appearance of dark gums. This may involve techniques such as laser therapy or surgical removal of the pigmented tissue.
Addressing Underlying Conditions
Treating any underlying medical conditions contributing to gum discoloration is essential for long-term oral health.
Prevention
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Monitor Medications
- Early Intervention
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are crucial for preventing gum discoloration and associated complications.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Avoiding tobacco use and maintaining a balanced diet can contribute to overall gum health.
Monitor Medications
Be aware of potential side effects of medications and discuss any concerns with healthcare providers.
Early Intervention
Address gum discoloration promptly to prevent it from progressing to more severe oral health issues.
Conclusion
Black gums can be a cause for concern and should not be ignored. While genetic factors and certain medical conditions can contribute to gum discoloration, practicing good oral hygiene and seeking timely dental care are essential steps in preventing and managing this condition. Whether the discoloration is due to natural melanin deposits, lifestyle choices, or underlying health issues, taking proactive measures can lead to improved oral health and overall well-being. If you notice any changes in the color or appearance of your gums, it’s important to consult a dental professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment recommendations.