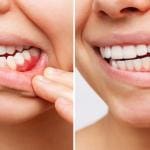
Gum health is a vital aspect of overall oral health, often overlooked but crucial for maintaining a beautiful smile and preventing serious dental issues. Healthy gums provide a strong foundation for your teeth and help in avoiding conditions like gum disease, tooth decay, and tooth loss. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the significance of gum health, the factors affecting it, how to maintain healthy gums, and how poor gum health can impact your overall well-being.
Understanding Gum Health
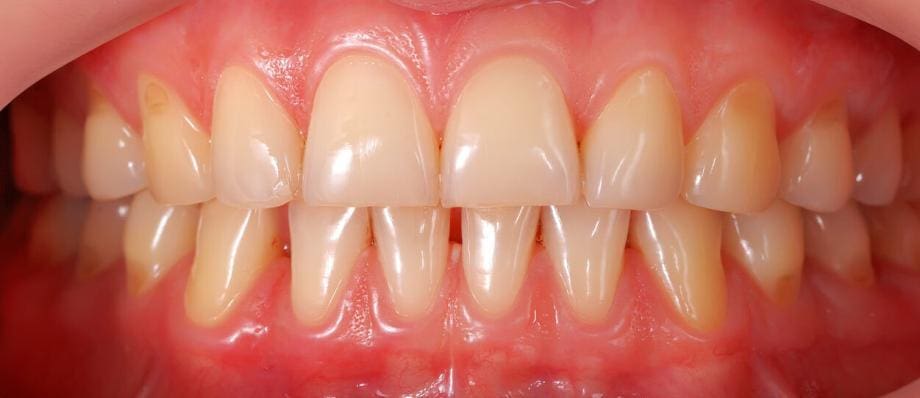
Gums, also known as gingiva, are the soft tissues that surround and support your teeth. They are composed of mucosal tissue and play a crucial role in maintaining your oral health. Healthy gums should be firm, pale pink, and fit snugly around the teeth without any signs of redness, swelling, or bleeding.
Importance of Gum Health
- Support for Teeth
- Preventing Gum Disease
- Aesthetic Value
- Overall Well-being
Support for Teeth
Healthy gums provide essential support to your teeth by holding them in place. They create a seal around the teeth, preventing harmful bacteria from infiltrating the roots and causing damage.
Preventing Gum Disease
Proper gum health is the primary defense against gum disease or periodontal disease, which is a bacterial infection that affects the gums and the bones supporting the teeth.
Aesthetic Value
Healthy gums contribute to an attractive smile. Red, swollen, or bleeding gums can be unattractive and diminish the appearance of your teeth.
Overall Well-being
Research indicates a link between gum health and overall health. Poor gum health has been associated with various systemic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Factors Affecting Gum Health
Several factors influence the health of your gums. Understanding these factors can help you take proactive steps in maintaining or improving your gum health.
- Oral Hygiene Practices
- Diet and Nutrition
- Tobacco Use
- Medical Conditions
- Hormonal Changes
- Genetics
Oral Hygiene Practices
Effective oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, are fundamental for gum health. Brushing removes plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, from the teeth and gums, while flossing helps clean between teeth where a toothbrush cannot reach.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet plays a significant role in maintaining gum health. Consuming a variety of nutrients, including vitamins and minerals, supports healthy gums and helps prevent gum disease. Vitamin C is particularly essential for gum health.
Tobacco Use
Tobacco use, including smoking and chewing tobacco, is a significant risk factor for gum disease. It interferes with the healing process, weakens the immune system, and increases the risk of gum infections.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune disorders can affect gum health. Individuals with diabetes are more prone to gum disease due to impaired blood sugar control.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can affect the gums, making them more susceptible to gum disease. It’s crucial to maintain good oral hygiene during these periods.
Genetics
Genetics can influence the susceptibility to gum disease. If your family has a history of gum problems, you may be at a higher risk.
Maintaining Healthy Gums
Achieving and maintaining healthy gums involves a combination of proper oral hygiene, a balanced diet, regular dental check-ups, and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some effective strategies:
- Brush and Floss Regularly
- Use Mouthwash
- Balanced Diet
- Regular Dental Check-ups
- Quit Tobacco
- Manage Stress
- Stay Hydrated
- Use a Soft Toothbrush
Brush and Floss Regularly
Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush. Additionally, floss once a day to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth.
Use Mouthwash
Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash that can help reduce plaque and gingivitis. Consult your dentist to find the right mouthwash for your needs.
Balanced Diet
Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy. Avoid sugary and sticky foods that can contribute to plaque formation and gum disease.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Visit your dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings. Professional cleanings help remove tartar and plaque that cannot be eliminated with regular brushing and flossing.
Quit Tobacco
If you use tobacco, consider quitting. Seek support and resources to help you quit smoking or chewing tobacco, as it significantly impacts gum health.
Manage Stress
Stress can affect your immune system and potentially lead to gum problems. Practice stress-relieving techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Water helps in washing away food particles and bacteria that can contribute to gum disease.
Use a Soft Toothbrush
Opt for a soft-bristled toothbrush to prevent irritation and damage to your gums while brushing.
Consequences of Poor Gum Health
Neglecting your gum health can have serious consequences, impacting not only your oral health but also your overall well-being.
- Gum Disease (Periodontitis)
- Tooth Decay
- Bad Breath (Halitosis)
- Tooth Sensitivity
- Systemic Health Issues
Gum Disease (Periodontitis)
Untreated gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. It can lead to bone and tooth loss, affecting your ability to chew and speak.
Tooth Decay
Gum disease can contribute to tooth decay as the gums recede, exposing the tooth roots to bacteria and decay.
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Gum disease often causes persistent bad breath, which can be socially embarrassing and indicate underlying dental problems.
Tooth Sensitivity
Receding gums can expose the tooth roots, resulting in increased tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks.
Systemic Health Issues
Research suggests a link between gum disease and systemic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and complications during pregnancy. Poor gum health can exacerbate these conditions.
Community Involvement and Oral Health Education
Promoting gum health involves not only personal care but also community involvement and education. Oral health education initiatives can significantly impact individuals’ understanding of gum health and their willingness to adopt healthy oral habits.
School Programs
Introducing oral health education in schools can establish lifelong habits in children. Teaching them about proper brushing techniques, the importance of regular dental check-ups, and a healthy diet can lay a strong foundation for maintaining gum health throughout their lives.
Community Workshops and Seminars
Organizing workshops and seminars in local communities can raise awareness about gum health. Dental professionals can conduct sessions to educate the public about the significance of healthy gums, how to achieve it, and the consequences of neglecting gum health.
Collaboration with Healthcare Providers
Collaborations between dental professionals and other healthcare providers, such as general physicians and nutritionists, can enhance comprehensive healthcare. Integrated care that addresses both systemic health and oral health can have a positive impact on gum health.
Utilizing Social Media and Online Platforms
Leveraging social media and online platforms to disseminate information about gum health can reach a broader audience. Dental professionals can share tips, videos, and infographics to educate people about maintaining healthy gums and seeking timely dental care.
Engaging in Public Campaigns
Participating in public campaigns dedicated to oral health, such as National Dental Health Month, can highlight the importance of gum health. These campaigns can encourage individuals to prioritize their oral health and seek regular dental check-ups.
The Role of Policy and Legislation
Government policies and legislation play a crucial role in promoting gum health at a population level. Here are some ways policymakers can contribute to improving gum health:
- Incorporate Oral Health in Public Health Agendas
- Provide Accessible Dental Care
- Education and Awareness Programs
- Regulation of Tobacco Products
Incorporate Oral Health in Public Health Agendas
Including oral health in public health agendas emphasizes the importance of dental care and encourages its integration into overall healthcare systems. This integration ensures that oral health, including gum health, is given due attention and resources.
Provide Accessible Dental Care
Government programs and policies should strive to make dental care, including routine check-ups and preventive measures, accessible and affordable to all segments of the population. This ensures that individuals can receive the necessary care to maintain healthy gums.
Education and Awareness Programs
Government initiatives should support educational programs aimed at raising awareness about the importance of gum health and providing information on how to maintain it. This can lead to a decrease in the prevalence of gum disease.
Regulation of Tobacco Products
Implementing strict regulations on tobacco products, including raising taxes, restricting advertising, and enforcing clear warning labels, can discourage the use of tobacco, which is a significant risk factor for gum disease.
Emerging Trends and Future Prospects
As dental and medical research advances, new trends and technologies are emerging to promote gum health and tackle gum-related issues. Understanding these trends can guide individuals in making informed decisions about their oral health.
- Telehealth and Teledentistry
- Personalized Oral Care
- Regenerative Dentistry
- AI and Machine Learning
- Smart Oral Health Devices
- Natural and Holistic Approaches
Telehealth and Teledentistry
Advancements in telehealth have extended to dentistry, enabling remote consultations and advice on maintaining gum health. Teledentistry allows individuals to consult with oral health professionals, share symptoms, and receive recommendations without physically visiting a dental clinic.
Personalized Oral Care
Genetic testing and personalized medicine are gaining traction in dentistry. Genetic analysis can provide insights into an individual’s predisposition to certain oral health issues, including gum disease. This allows for tailored preventive strategies and treatments.
Regenerative Dentistry
Regenerative dentistry focuses on restoring damaged gums and other oral tissues. Techniques such as stem cell therapy, tissue engineering, and growth factors are being explored to regenerate gum tissue and bone, potentially revolutionizing the treatment of gum disease.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being used to analyze oral health data, predict gum disease progression, and optimize treatment plans. AI algorithms can help dentists identify early signs of gum disease, allowing for timely interventions and improved outcomes.
Smart Oral Health Devices
Smart toothbrushes and oral health apps equipped with sensors and AI capabilities are becoming popular. These devices can provide real-time feedback on brushing techniques, track oral hygiene habits, and remind users to maintain regular oral care routines.
Natural and Holistic Approaches
Growing interest in natural and holistic approaches to oral health is encouraging the use of essential oils, herbal remedies, and natural products for gum care. These approaches emphasize overall wellness and a balance between traditional dental care and natural alternatives.
Conclusion
Achieving and maintaining healthy gums is a lifelong commitment that requires diligence, knowledge, and a proactive approach. By understanding the importance of gum health, recognizing the factors that influence it, and actively participating in oral health education and initiatives, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and preserve their smiles for years to come.
Remember, healthy gums are not only aesthetically pleasing but also indicative of good oral and systemic health. Embrace a gum-friendly lifestyle, seek professional dental care regularly, and actively engage with your community to spread awareness about the significance of gum health. Together, we can work towards a world where healthy gums and smiles are a priority for all.