Periodontitis, also known as gum disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. It is a serious condition that, if left untreated, can lead to tooth loss and have a significant impact on overall health. This comprehensive article will delve into the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures for periodontitis.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Periodontitis
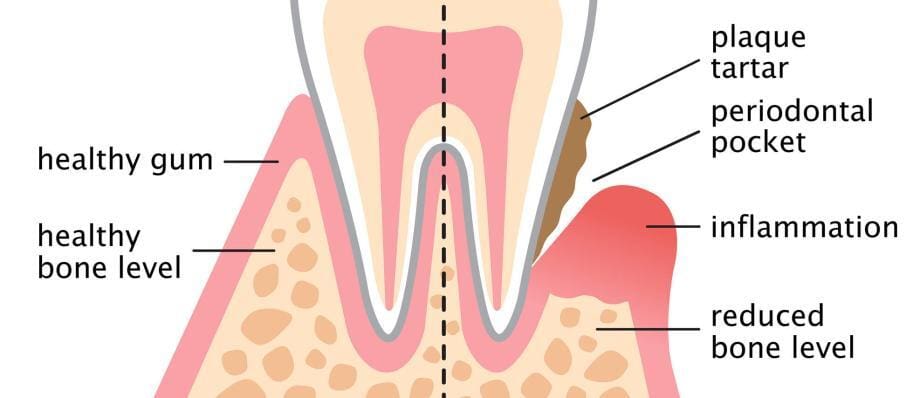
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the supporting structures of the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone. It is primarily caused by bacteria present in dental plaque, a sticky film that forms on the teeth. The bacteria release toxins that irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and destruction of the supporting tissues.
Causes of Periodontitis
Several factors contribute to the development of periodontitis:
- Poor Oral Hygiene
- Tobacco Use
- Genetic Predisposition
- Hormonal Changes
- Systemic Diseases
Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing, flossing, and lack of regular dental check-ups can lead to the accumulation of plaque, which contributes to the development of gum disease.
Tobacco Use
Smoking and tobacco consumption are significant risk factors for periodontitis. These habits impair blood flow to the gums, weaken the immune system, and make it more difficult for the body to fight off infections.
Genetic Predisposition
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing periodontitis. Certain genetic variations affect the immune response, making individuals more susceptible to gum disease.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make the gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation, increasing the risk of periodontitis.
Systemic Diseases
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and HIV/AIDS, can impair the body’s ability to fight off infections, including gum disease.
Symptoms of Periodontitis
Periodontitis often progresses slowly and may initially be painless, making it essential to be aware of the following symptoms:
- Red, Swollen Gums
- Bleeding Gums
- Receding Gums
- Persistent Bad Breath
- Tooth Sensitivity
- Loose or Shifting Teeth
Red, Swollen Gums
Inflamed gums that appear red and swollen are an early sign of gum disease.
Bleeding Gums
Gums that bleed during brushing, flossing, or even spontaneously, indicate a problem.
Receding Gums
As periodontitis advances, the gum line may start to recede, exposing the tooth roots.
Persistent Bad Breath
Bacteria in the mouth release foul-smelling gases, causing chronic bad breath.
Tooth Sensitivity
Periodontitis can lead to tooth sensitivity, especially to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli.
Loose or Shifting Teeth
In advanced stages, periodontitis can cause tooth mobility or changes in the alignment of the teeth.
Treatment Options
Timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing periodontitis. The treatment plan may involve the following:
- Professional Dental Cleaning
- Medications
- Surgery
- Ongoing Maintenance
Professional Dental Cleaning
A dental professional will perform a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line.
Medications
Antibiotics, antimicrobial mouth rinses, or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to control bacterial infection and inflammation.
Surgery
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures such as flap surgery, bone grafts, and tissue regeneration can help restore damaged tissues and support the teeth.
Ongoing Maintenance
Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor progress, remove any plaque buildup, and maintain good oral hygiene.
Preventive Measures
Preventing periodontitis involves adopting good oral hygiene practices and minimizing risk factors:
- Brushing and Flossing
- Regular Dental Check-ups
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Manage Systemic Health
- Hormonal Considerations
Brushing and Flossing
Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled brush and use dental floss or interdental brushes to clean between the teeth and along the gum line.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Visit your dentist for regular check-ups and professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar.
Healthy Lifestyle
Avoid tobacco use and maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and low in sugary snacks and beverages.
Manage Systemic Health
Control conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and HIV/AIDS, as they can impact oral health.
Hormonal Considerations
During periods of hormonal fluctuations, such as pregnancy, practice diligent oral hygiene and inform your dentist to address any concerns.
The Link Between Periodontitis and Overall Health
Beyond its impact on oral health, periodontitis has been associated with several systemic health conditions. Research has shown a correlation between gum disease and the following conditions:
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Diabetes
- Respiratory Infections
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Pregnancy Complications
Cardiovascular Disease
Studies suggest that periodontitis may increase the risk of developing heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. The inflammation caused by gum disease can contribute to the formation of plaques in the arteries and the progression of atherosclerosis.
Diabetes
Individuals with diabetes are more prone to developing periodontitis. Conversely, gum disease can make it challenging to control blood sugar levels, leading to complications in diabetic individuals. Maintaining good oral health is crucial in managing diabetes effectively.
Respiratory Infections
The bacteria associated with periodontitis can be inhaled into the lungs, potentially causing respiratory infections like pneumonia. This is particularly concerning for individuals with compromised immune systems.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Some studies have found a link between gum disease and rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder that causes joint inflammation. The exact relationship between the two conditions is still being investigated, but it is believed that the systemic inflammation triggered by periodontitis may contribute to the development or worsening of arthritis symptoms.
Pregnancy Complications
Pregnant women with untreated periodontitis may have an increased risk of premature birth, low birth weight, and preeclampsia. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can make the gums more susceptible to inflammation and infection, highlighting the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene during this period.
Oral Hygiene and Periodontitis Prevention
Preventing periodontitis starts with establishing and maintaining proper oral hygiene practices. Here are some key steps to follow:
- Brushing Technique
- Flossing
- Mouthwash
- Healthy Diet
- Tobacco and Alcohol
- Regular Dental Visits
Brushing Technique
Brush your teeth at least twice a day for two minutes each time. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Hold the brush at a 45-degree angle to your gum line and brush gently in circular motions, ensuring that you clean the outer, inner, and chewing surfaces of the teeth.
Flossing
Clean between your teeth using dental floss or interdental brushes. Flossing removes plaque and food particles from areas that a toothbrush cannot reach effectively.
Mouthwash
Rinse your mouth with an antimicrobial mouthwash daily to reduce bacteria and freshen your breath.
Healthy Diet
Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products. Limit sugary snacks and beverages, as sugar contributes to plaque formation.
Tobacco and Alcohol
Avoid tobacco use, as it significantly increases the risk of gum disease. Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive alcohol intake can harm oral tissues and impair immune function.
Regular Dental Visits
Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings. Your dentist can detect early signs of gum disease and provide appropriate treatment before it progresses.
Education and Awareness
Promoting education and awareness about periodontitis is crucial in preventing and managing the disease. Dentists and dental hygienists play a vital role in educating patients about proper oral hygiene practices, the importance of regular dental visits, and the early signs of gum disease.
Additionally, public health campaigns, community outreach programs, and educational resources should emphasize the significance of maintaining good oral health, including the prevention and treatment of periodontitis. By raising awareness, individuals can make informed decisions about their oral hygiene habits and seek timely dental care when necessary.
Conclusion
Periodontitis is a prevalent oral health condition that affects the supporting structures of the teeth. It can have serious consequences on both oral health and overall well-being if left untreated. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can reduce the risk of developing gum disease and its associated health complications.
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, visiting the dentist regularly, and adopting a healthy lifestyle are essential in preventing and managing periodontitis. Furthermore, it is crucial to be aware of the potential links between gum disease and systemic health conditions, as this highlights the significance of oral health in maintaining overall well-being.
By prioritizing oral health and seeking timely treatment for periodontitis, individuals can preserve their teeth, maintain a healthy smile, and contribute to their long-term health and quality of life. Remember, a healthy mouth is a gateway to a healthy body.

zoritoler imol
13 June 2024obviously like your website but you have to check the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I find it very bothersome to tell the reality then again I’ll certainly come again again.