Maintaining good oral health goes beyond brushing and flossing. The foods we consume play a significant role in the condition of our teeth and gums. While some foods promote healthy gums, others can irritate or even harm them, leading to discomfort, swelling, or more serious oral health problems. In this article, we’ll explore the foods that irritate gums, why they cause issues, and how to make better dietary choices to support your oral health.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Gum Irritation
Gum irritation is characterized by redness, swelling, bleeding, or sensitivity in the gum tissue. This irritation can be caused by several factors, including poor oral hygiene, underlying medical conditions, or consuming certain foods. When food particles become trapped between the teeth and gums, they can feed harmful bacteria, exacerbating gum problems.
While some foods naturally aggravate gums due to their texture or composition, the way these foods interact with existing conditions, such as gingivitis or periodontitis, can magnify their effects. Being mindful of what you eat is key to maintaining gum health.
Common Foods That Irritate Gums
1. Sugary Foods and Beverages
Sugar is one of the leading culprits when it comes to oral health issues, including gum irritation. When you consume sugary foods like candies, pastries, or sodas, sugar residues stick to your teeth and gums, providing a feast for harmful bacteria. As these bacteria break down sugar, they produce acids that irritate gums and erode enamel.
Examples of sugary irritants:
- Hard candies (e.g., lollipops)
- Gummy candies
- Sugary sodas and energy drinks
- Frosted cakes and cookies
These foods not only irritate gums but also increase the risk of cavities and gum disease over time.
2. Acidic Foods and Beverages
Highly acidic foods and drinks can cause gum irritation and exacerbate sensitivity. Acidic substances weaken the enamel and make gums more vulnerable to irritation and infection. Prolonged exposure to acidic foods can also lead to gum recession.
Examples of acidic irritants:
- Citrus fruits (e.g., oranges, lemons, and grapefruits)
- Tomato-based products (e.g., ketchup, pasta sauces)
- Vinegar-based foods (e.g., pickles, salad dressings)
- Carbonated drinks
Acidic foods can also cause a burning sensation for people with sensitive gums or oral sores, making them doubly problematic.
3. Spicy Foods
Spices, while flavorful, can cause significant discomfort for individuals with sensitive gums or existing oral conditions. The capsaicin in spicy foods can irritate tissues in the mouth and aggravate gum inflammation.
Examples of spicy irritants:
- Hot peppers (e.g., jalapeños, habaneros)
- Spicy sauces (e.g., sriracha, hot wings sauce)
- Heavily spiced snacks (e.g., chili-flavored chips)
While occasional spice is unlikely to cause lasting damage, regular consumption can worsen symptoms of gum disease and irritate sores or cuts in the mouth.
4. Crunchy and Hard Foods
Crunchy foods can scrape against the gums, causing micro-abrasions that may lead to irritation, swelling, or bleeding gums. If you already have sensitive gums or gum disease, crunchy foods can exacerbate discomfort or even lead to infections.
Examples of crunchy irritants:
- Chips and pretzels
- Hard bread crusts (e.g., baguettes)
- Nuts (e.g., almonds, walnuts)
- Popcorn (particularly unpopped kernels)
Unpopped popcorn kernels and hard nuts are especially risky, as they can become lodged between the gums and teeth, creating a breeding ground for bacteria.
5. Sticky Foods
Sticky foods tend to cling to the teeth and gums, making them difficult to clean off. This prolonged contact allows bacteria to thrive, potentially leading to gum irritation or tooth decay.
Examples of sticky irritants:
- Caramel and taffy
- Dried fruits (e.g., raisins, apricots)
- Chewing gum (especially sugar-laden varieties)
- Sticky rice or glutinous foods
Sticky residues can also forcefully pull on the gums during chewing, adding to discomfort or inflammation.
6. Highly Processed Foods
Many processed foods are packed with artificial flavors, preservatives, and chemicals that can irritate gums. These foods often lack the nutrients needed for gum health and may exacerbate existing issues.
Examples of processed irritants:
- Packaged snacks (e.g., flavored crackers, instant noodles)
- Fast food
- Processed meats (e.g., salami, bacon)
- Sugary breakfast cereals
The high salt and sugar content in processed foods contributes to dehydration and a lack of saliva, which is essential for washing away irritants from the gums.
7. Alcohol
Alcoholic beverages can dry out the mouth, reducing saliva production. A dry mouth creates an environment where bacteria can thrive, leading to gum irritation and bad breath. Certain alcohols, like wine or beer, are also acidic and can further weaken gum tissue.
Examples of alcoholic irritants:
- Wine (red and white)
- Beer
- Spirits (e.g., vodka, whiskey)
- Cocktails with sugary mixers
Over time, chronic alcohol consumption can lead to more serious oral health issues, such as gum disease or oral cancer.
8. Hot Foods and Beverages
Extremely hot foods and drinks can scald the gums, causing inflammation or burns. This damage not only irritates the gums but also leaves them vulnerable to infections.
Examples of hot irritants:
- Piping hot soups or stews
- Coffee or tea served at high temperatures
- Freshly baked pizzas or pies
To protect your gums, allow hot foods and beverages to cool before consuming them.
9. Allergenic Foods
Certain foods can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals, leading to gum swelling and irritation. If you notice your gums reacting to specific foods, you may need to consult a healthcare provider for an allergy test.
Examples of potential allergens:
- Shellfish
- Nuts
- Dairy products
- Soy
Allergic reactions in the mouth may also involve itching, hives, or a burning sensation.
Why Do These Foods Irritate Gums?
Gum irritation from foods typically occurs due to one or more of the following factors:
- Texture – Hard or sharp-edged foods can physically damage gum tissue.
- Chemical composition – Sugars, acids, and spices interact negatively with gum tissues or feed harmful bacteria.
- Residual effects – Sticky or sugary foods linger on the teeth and gums, exacerbating bacterial growth.
- Drying effects – Certain foods and beverages reduce saliva production, increasing susceptibility to irritation.
Preventing Gum Irritation from Food
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene – Brush twice daily, floss regularly, and use an antibacterial mouthwash to remove food particles and bacteria.
- Stay Hydrated – Drink plenty of water to wash away food particles and maintain healthy saliva levels.
- Rinse After Eating – Rinsing your mouth with water or a saline solution after meals can help remove irritants and soothe gums.
- Eat a Balanced Diet – Include foods rich in vitamins C, D, and calcium, which support gum health.
- Chew Mindfully – Avoid biting into hard or sharp-edged foods that could damage your gums.
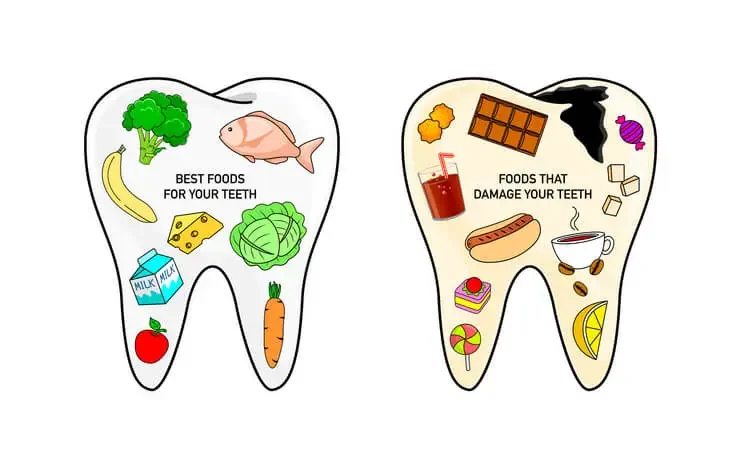
Foods That Promote Healthy Gums
Instead of consuming irritants, opt for foods that actively support gum health:
- Leafy greens – Spinach and kale are rich in vitamins that reduce inflammation.
- Dairy products – Milk, yogurt, and cheese provide calcium and phosphate for strong teeth and gums.
- Crunchy vegetables – Carrots and celery help clean teeth naturally and stimulate saliva production.
- Fruits rich in vitamin C – Strawberries and kiwis support collagen production, which is essential for gum tissue.
- Green tea – Contains antioxidants that fight bacteria and reduce inflammation.
When to See a Dentist
If you experience persistent gum irritation, redness, or bleeding, it’s essential to consult a dentist near you. Gum irritation caused by food can sometimes be a sign of an underlying condition, such as gingivitis or periodontitis, which requires professional intervention.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can these foods cause long-term gum damage?
Yes, frequent consumption of irritating foods can lead to chronic gum problems, including gingivitis and periodontitis. Over time, repeated irritation can contribute to gum recession and tooth sensitivity.
Are there any foods that help soothe irritated gums?
Yes! Foods that promote gum health include:
- Leafy greens (rich in vitamins that reduce inflammation)
- Dairy products (calcium supports strong teeth and gums)
- Crunchy vegetables (like carrots and celery, which help clean teeth naturally)
- Green tea (contains antioxidants that fight bacteria and reduce inflammation)
How can I reduce gum irritation after eating these foods?
To minimize gum irritation:
- Rinse your mouth with water or an alcohol-free mouthwash after eating.
- Brush and floss regularly to remove food particles.
- Chew sugar-free gum to stimulate saliva production.
- Stay hydrated to keep your mouth moist and wash away irritants.
Why does my gum irritation worsen after eating certain foods?
If your gums are particularly sensitive, acidic, spicy, or hard foods can intensify irritation. You may also have an underlying condition like gingivitis, gum recession, or an allergy that makes your gums more reactive to certain foods.
When should I see a dentist about gum irritation?
You should visit a dentist if:
- Your gums bleed frequently, even when brushing gently.
- You experience persistent gum pain or swelling.
- You have sores or ulcers that don’t heal.
- Your gums appear receded or inflamed for long periods.
Early intervention can prevent minor irritation from becoming a serious gum disease.
Conclusion
Your diet has a profound impact on your oral health. While some foods can irritate gums and exacerbate oral issues, others can nourish and protect your gums. By understanding which foods to avoid and adopting healthier dietary habits, you can reduce gum irritation and improve your overall oral health. Always prioritize good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups to keep your gums healthy and pain-free.