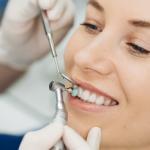
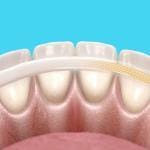
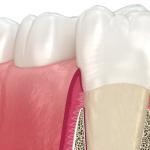
Receding gums, also known as gingival recession, is a common dental problem that affects many people worldwide. It occurs when the gum tissue that surrounds and supports the teeth pulls back, exposing the tooth roots and sometimes causing tooth sensitivity or even tooth loss.
This condition can affect anyone, but it is most common among adults over 40 years of age. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for receding gums.
Causes of Receding Gums
There are several reasons why gums may recede. Some of the most common causes of gum recession include:
- Gum disease
- Brushing too hard
- Tooth grinding
- Poor oral hygiene
- Genetics
- Hormonal changes
- Smoking
- Trauma
- Poor orthodontic treatment plan
- High frenulum attachment
Gum disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the gum tissue and bone that support the teeth. As the infection progresses, it can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth, leading to receding gums.
Brushing too hard
Brushing your teeth too vigorously can cause the enamel on your teeth to wear away and your gums to recede.
Tooth grinding
also known as bruxism, can also be a contributing factor to receding gums. Bruxism can put excessive pressure on the teeth and gums, which can lead to gum recession over time. The constant grinding and clenching of the teeth can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth and expose the tooth roots, leading to sensitivity and other oral health problems.
Poor oral hygiene
Poor oral hygiene can cause plaque buildup and calculus accumulation, which can lead to gum disease and ultimately, receding gums.
Genetics
Some people are more prone to gum disease and receding gums due to their genetics.
Hormonal changes
Hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause can cause the gums to become more sensitive and prone to receding.
Smoking
Smoking can cause gum disease and increase the risk of receding gums.
Trauma
Trauma to the gums, such as an injury or accident, can cause the gum tissue to recede.
Poor orthodontic treatment plan
In some cases, orthodontic treatment may cause the teeth to move too quickly or in the wrong direction, which can put excessive pressure on the gums and lead to recession.
High frenulum attachment
Also known as a frenum, can contribute to gum recession as well. The frenulum is a small fold of tissue that connects the lips, cheeks, or tongue to the gums or the floor of the mouth. When the frenulum is attached too high on the gums, it can put excessive pressure on the gums and cause them to recede.
Symptoms of Receding Gums
The symptoms of receding gums may vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Teeth that appear longer than usual
- A noticeable gap between the teeth and gums
- Tooth sensitivity or pain
- Bleeding gums
- Bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
- Loose teeth or teeth that are shifting
Treatment for Gum Recession
The treatment for receding gums depends on the severity of the condition. Some of the most common treatment options include:
- Scaling and root planing
- Gum grafting
- Mouthguard
- Pocket reduction surgery
- Orthodontic treatment
- Good oral hygiene
- Ferenectomy
Scaling and root planing
Scaling and root planing is a deep teeth cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar buildup from the teeth and roots. This can help prevent further gum recession and gum disease.
Gum grafting
Gum grafting is a surgical procedure that involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth and attaching it to the receded gum area. This can help restore the gum tissue and protect the tooth roots.
Mouthguard
If you suspect that you are grinding your teeth, it is important to speak with your dentist. Your dentist may recommend a custom mouthguard or splint to wear at night, which can help protect your teeth and gums from the damaging effects of bruxism. Additionally, your dentist may suggest stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or exercise, to help manage your bruxism and prevent further damage to your gums and teeth.
Pocket reduction surgery
Pocket reduction surgery is a procedure that involves removing the bacteria and infected tissue from the gum pockets around the teeth. This can help reduce the risk of further gum recession and bone loss.
Orthodontic treatment
Orthodontic treatment, such as braces or aligners, can help correct the alignment of the teeth and prevent further gum recession.
Good oral hygiene
Maintaining good oral hygiene, such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly, can help prevent gum disease and receding gums.
Ferenectomy
A high frenulum attachment may require a surgical procedure called a frenectomy. During this procedure, the frenulum is removed or repositioned to relieve the pressure on the gums and prevent further gum recession. Your dentist or periodontist can determine if a frenectomy is necessary based on your individual needs and oral health status.
Preventing Receding Gums
Preventing receding gums starts with good oral hygiene practices. This includes:
- Brushing twice a day
- Flossing daily
- Using mouthwash
- Visiting the dentist regularly
- Quitting smoking
- Eating a balanced diet
- Managing stress
- Choosing a qualified orthodontist
- Removing high ferenulum attachments
Brushing twice a day
Brush your teeth twice a day for two minutes each time using a soft-bristled toothbrush.
Flossing daily
Floss your teeth at least once a day to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and gums.
Using mouthwash
Use an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen your breath.
Visiting the dentist regularly
Visit your dentist every six months for a checkup and professional cleaning.
Quitting smoking
Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of gum disease and receding gums.
Eating a balanced diet
Eating a healthy and balanced diet can provide your body with the nutrients it needs to maintain healthy gums and teeth.
Managing stress
Stress can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of gum disease. Managing stress through activities like yoga or meditation can help reduce the risk of receding gums.
Choosing a qualified orthodontist
It is important to work with an experienced and qualified orthodontist who will take a comprehensive approach to your treatment plan, considering not only the straightening of your teeth but also the health of your gums and other oral structures.
Removing high ferenulum attachments
It is important to address any potential risk factors for gum recession, including a high frenulum attachment, as early as possible to prevent further damage to your gums and teeth.
Complications of Gum Recession
If left untreated, receding gums can lead to a variety of complications, including:
- Tooth loss
- Gum disease
- Sensitivity
- Aesthetic concerns
Tooth loss
Severe gum recession can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
Gum disease
Receding gums can increase the risk of gum disease, which can lead to further gum recession and tooth loss.
Sensitivity
Exposed tooth roots can cause tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks.
Aesthetic concerns
Receding gums can make the teeth look longer than usual, which can affect the appearance of your smile.
Conclusion
Receding gums is a common dental problem that can lead to a variety of complications if left untreated. The condition can be caused by factors such as gum disease, brushing too hard, poor oral hygiene, genetics, hormonal changes, smoking, and trauma. The symptoms of receding gums may include tooth sensitivity, bleeding gums, bad breath, and loose teeth. Treatment options for receding gums may include scaling and root planing, gum grafting, pocket reduction surgery, orthodontic treatment, and good oral hygiene practices. Preventing receding gums starts with maintaining good oral hygiene practices, quitting smoking, eating a balanced diet, and managing stress. If you notice any symptoms of receding gums, it is important to see your dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.