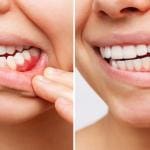
Crown lengthening is a dental procedure designed to expose more of a tooth’s structure by removing gum tissue and bone around the tooth. It is commonly performed by periodontists, specialists in treating the gums and supporting structures of teeth. This procedure can serve both functional and aesthetic purposes, aiding in various dental treatments and enhancing the appearance of a person’s smile.
Purpose of Crown Lengthening
- Functional Reasons
- Aesthetic Reasons
Functional Reasons
Crown lengthening is often performed to facilitate other dental procedures. It may be necessary if a tooth is broken near the gumline, decayed below the gumline, or if there isn’t enough tooth structure available for a restoration like a crown or a bridge. By exposing more of the tooth, the dentist gains better access to the area needed for restorative work.
Aesthetic Reasons
In some cases, crown lengthening is performed for cosmetic purposes. It can improve the appearance of a “gummy smile,” where excess gum tissue makes teeth appear shorter. By reshaping the gums and exposing more of the tooth’s surface, the smile can be enhanced, creating a more balanced and attractive look.
Crown Lengthening Procedure
- Evaluation
- Anesthesia
- Tissue Removal
- Suturing
- Recovery
- Follow-Up
Evaluation
Before the procedure, a thorough examination is conducted by the dentist to assess the need for crown lengthening. X-rays might be taken to determine the amount of bone around the tooth and the location of adjacent structures like nerves.
Anesthesia
The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia to numb the area being treated. Sedation might be used for anxious patients or for more extensive procedures.
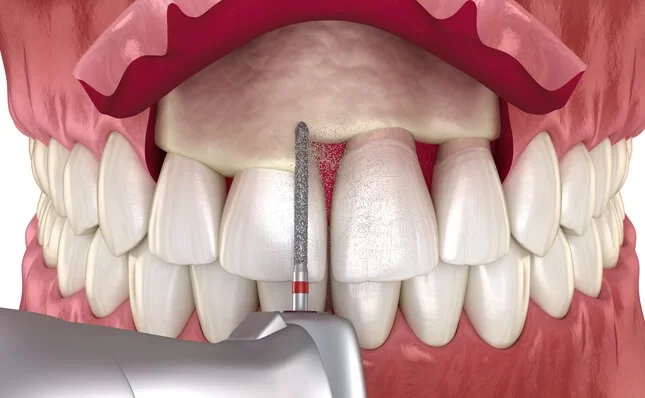
Tissue Removal
Once the area is numb, the periodontist makes small incisions in the gums to access the underlying bone and tooth structure. They carefully remove excess gum tissue and, if necessary, reshape the bone around the tooth to expose more of the tooth’s surface.
Suturing
After the necessary adjustments are made, the gums are stitched back into place with dissolvable sutures.
Recovery
Recovery time varies from person to person and depends on the extent of the procedure. Patients might experience some discomfort, swelling, and minor bleeding immediately after the surgery. Pain medications and antibiotics might be prescribed by the dentist to manage post-operative symptoms. Patients are usually advised to stick to a soft diet and avoid strenuous activities for a few days to aid in the healing process.
Follow-Up
Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor the healing progress. The dentist will remove the sutures and ensure that the gums are healing properly.
Benefits of Crown Lengthening
- Improved Dental Health
- Restoration Support
- Enhanced Aesthetics
Improved Dental Health
Crown lengthening can enhance oral health by allowing better access for cleaning and maintaining the tooth structure. It reduces the risk of decay and periodontal disease by making it easier to keep the area free of plaque and bacteria.
Restoration Support
The procedure provides a solid foundation for restorative treatments like crowns, bridges, or fillings. By exposing more of the tooth, there is ample space for the placement of these dental restorations, ensuring their longevity and effectiveness.
Enhanced Aesthetics
From a cosmetic perspective, crown lengthening can significantly improve the appearance of a smile. By balancing the proportion of teeth to gums, it can create a more symmetrical and aesthetically pleasing smile.
Risks and Considerations
Like any surgical procedure, crown lengthening carries some risks. These may include:
- Pain and Discomfort
- Infection
- Sensitivity
- Gum Recession
Pain and Discomfort
Some discomfort and swelling are expected after the procedure. Pain medications are usually prescribed to manage this.
Infection
Proper oral hygiene and following post-operative instructions can minimize the risk of infection.
Sensitivity
Exposed tooth surfaces may become sensitive to hot or cold temperatures. This sensitivity usually subsides as the gums heal.
Gum Recession
In some cases, over time, there might be a slight recession of the gums, exposing more of the tooth’s root. Proper oral hygiene can help prevent this.
Types of Crown Lengthening
- Functional Crown Lengthening
- Aesthetic Crown Lengthening
Functional Crown Lengthening
This type of crown lengthening is primarily aimed at restoring damaged teeth or teeth with insufficient structure for restorative procedures. It involves removing gum tissue and bone to expose more of the tooth, enabling the dentist to place a crown or bridge effectively. Functional crown lengthening helps in maintaining a healthy tooth-to-gum ratio, ensuring proper functionality of the affected tooth.
Aesthetic Crown Lengthening
Aesthetic crown lengthening focuses on improving the appearance of the smile. It’s often chosen by individuals with excessive gum tissue that makes their teeth appear short or uneven. By reshaping the gums and exposing more of the tooth’s surface, this procedure enhances the symmetry and balance of the smile, leading to a more pleasing aesthetic outcome.
Candidates for Crown Lengthening
- Restorative Needs
- Cosmetic Enhancement
- Oral Health Concerns
Restorative Needs
Patients requiring extensive decay removal or a damaged tooth restoration may benefit from crown lengthening to expose more of the tooth structure for effective placement of restorations.
Cosmetic Enhancement
Individuals with a “gummy smile” or uneven gum line may opt for crown lengthening to achieve a more proportionate and aesthetically pleasing smile.
Oral Health Concerns
Patients with issues related to periodontal health, such as deep pockets around the teeth, might benefit from crown lengthening to improve access for better oral hygiene practices and prevent further gum disease.
Recovery and Aftercare
- Post-Operative Care
- Healing Time
- Long-Term Maintenance
Post-Operative Care
After the procedure, it’s essential to follow the dentist’s instructions diligently. This includes taking prescribed medications, adhering to a soft diet to avoid putting pressure on the treated area, and maintaining proper oral hygiene.
Healing Time
Complete healing typically takes a few weeks. During this period, it’s crucial to avoid irritating the treated area and to attend follow-up appointments as scheduled to monitor the healing progress.
Long-Term Maintenance
Regular dental check-ups are crucial post-crown lengthening. Proper oral hygiene practices, such as brushing, flossing, and using an antiseptic mouthwash, aid in maintaining the results and preventing complications.
Alternatives to Crown Lengthening
- Gum Contouring
- Orthodontic Treatment
Gum Contouring
For minor cases of excessive gum tissue, a less invasive procedure known as gum contouring or reshaping can be an alternative. This involves using a laser or scalpel to trim excess gum tissue without the need for bone removal.
Orthodontic Treatment
In some cases, orthodontic treatment, such as braces or aligners, can address certain aesthetic issues without the need for surgery. By gradually shifting the position of the teeth, orthodontic treatment can sometimes reduce the appearance of a gummy smile.
Conclusion
Crown lengthening is a valuable dental procedure that serves both functional and aesthetic purposes. It provides numerous benefits, including improved oral health, support for dental restorations, and enhanced smile aesthetics. While it involves some risks, proper post-operative care and regular dental visits can minimize these risks and ensure a successful outcome. If you’re considering crown lengthening, consult with a qualified dental professional to discuss the procedure’s suitability for your specific dental needs and goals.