When it comes to oral health, many people often focus solely on the appearance of their teeth, overlooking the critical role that gum health plays in maintaining overall oral hygiene. Neglecting gum health can lead to a range of oral and even systemic health issues. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the importance of gum health, its impact on overall well-being, and effective strategies to maintain healthy gums.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Gum Health
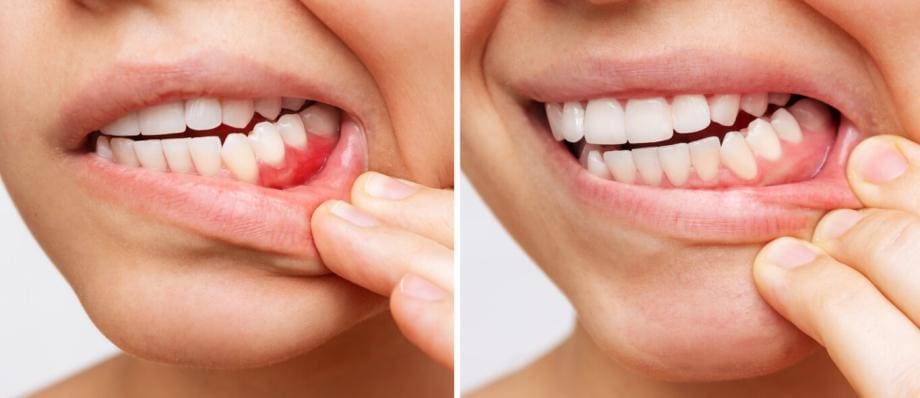
Gums, also known as gingiva, are the soft tissues that surround and support our teeth. They are made up of mucous membranes and connective tissues. Healthy gums are characterized by their pink color, firm texture, and the absence of bleeding or discomfort during brushing, flossing, or eating.
Gum health is directly linked to oral hygiene practices, diet, genetics, and overall health. Neglecting proper oral hygiene routines can lead to the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—on the teeth and gumline. Over time, if this plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar (calculus), which irritates the gums and leads to inflammation. This inflammation is known as gingivitis.
The Consequences of Poor Gum Health
- Gingivitis
- Periodontitis
- Systemic Health Implications
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums, particularly when brushing or flossing. Gingivitis is generally reversible with improved oral hygiene practices and professional dental cleanings.
Periodontitis
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to a more severe stage called periodontitis. This involves the infection of the deeper structures supporting the teeth, including the bone. Periodontitis can cause pockets to form between the teeth and gums, leading to further bacterial growth. As the condition worsens, it can result in tooth mobility and even tooth loss.
Systemic Health Implications
Emerging research suggests a strong connection between gum health and systemic health. Chronic inflammation in the gums can contribute to inflammation in other parts of the body, potentially increasing the risk of conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and even adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Strategies for Maintaining Gum Health
- Brushing
- Flossing
- Balanced Diet
- Limit Sugary Snacks and Beverages
- Regular Dental Check-ups
- Avoid Smoking
- Mouthwash
- Stress Management
Brushing
Regular brushing is crucial for gum health. Use a soft-bristle toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Brush gently in circular motions to remove plaque and debris from both the teeth and the gumline. Overly aggressive brushing can damage the gums, so it’s important to find a balance.
Flossing
Flossing removes food particles and plaque from between teeth and along the gumline, where a toothbrush can’t reach as effectively. Incorporate flossing into your daily routine to prevent the buildup of harmful bacteria.
Balanced Diet
A diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants is beneficial for gum health. Vitamin C, in particular, supports gum tissue health. Foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products provide essential nutrients for both teeth and gums.
Limit Sugary Snacks and Beverages
Sugary snacks and drinks can contribute to plaque formation, leading to gum issues and tooth decay. Limit your consumption of sugary foods and opt for healthier alternatives.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Professional dental cleanings and check-ups are essential for maintaining gum health. Dentists can identify early signs of gum disease and provide guidance on improving your oral hygiene routine.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease. It reduces blood flow to the gums, making it harder for them to heal and fight infections. Quitting smoking can have a positive impact on gum health.
Mouthwash
Using an antimicrobial or fluoride mouthwash can help reduce plaque and fight bacteria. However, it’s important to note that mouthwash is not a substitute for brushing and flossing.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections, including gum infections. Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
Signs of Healthy Gums
Recognizing the signs of healthy gums is just as important as understanding the consequences of poor gum health. Here are some indicators of good gum health:
- Pink Color
- Firm Texture
- No Bleeding
- Consistent Breath
Pink Color
Healthy gums are generally pink in color, although some individuals might have pigmentation variations.
Firm Texture
Gums should feel firm to the touch and not be excessively soft or swollen.
No Bleeding
Healthy gums should not bleed during brushing, flossing, or eating.
Consistent Breath
Foul breath can be a sign of bacterial activity in the mouth. Healthy gums contribute to fresher breath.
Taking Action: Building Healthy Habits
Maintaining healthy gums requires a combination of consistent oral care practices and lifestyle choices. Here are some actionable steps you can take to ensure optimal gum health:
- Establish a Consistent Routine
- Proper Brushing Technique
- Effective Flossing
- Choose the Right Products
- Balanced Nutrition
- Hydration
- Regular Dental Check-ups
- Stress Reduction
- Avoid Tobacco Products
- Educate Yourself
Establish a Consistent Routine
Consistency is key when it comes to gum health. Develop a daily oral hygiene routine that includes brushing, flossing, and rinsing with mouthwash. Stick to this routine to effectively remove plaque and prevent gum issues.
Proper Brushing Technique
While brushing is a basic practice, using the correct technique is essential. Hold your toothbrush at a 45-degree angle to your gums and use gentle, circular motions. Brush the fronts, backs, and tops of each tooth, as well as the gumline. Avoid harsh scrubbing, as it can harm the gums.
Effective Flossing
Flossing might seem tedious, but it’s a critical step in preventing gum disease. Gently slide the floss between your teeth and curve it around each tooth, reaching below the gumline. This helps remove trapped food particles and plaque.
Choose the Right Products
Select toothbrushes with soft bristles to avoid damaging your gums. Fluoride toothpaste helps strengthen teeth and prevent decay. When choosing a mouthwash, opt for one with antimicrobial properties to reduce bacteria in the mouth.
Balanced Nutrition
A diet rich in nutrients promotes gum health. Vitamin C, present in citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers, supports collagen production, which is vital for gum tissue integrity. Calcium and vitamin D are essential for maintaining strong teeth and bones.
Hydration
Drinking plenty of water helps flush away food particles and bacteria that can contribute to gum problems. Water also maintains saliva production, which is crucial for neutralizing acids and protecting teeth and gums.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Schedule regular dental appointments for professional cleanings and check-ups. Dentists can identify early signs of gum disease and provide personalized recommendations for improving your oral care routine.
Stress Reduction
Chronic stress can compromise your immune system and exacerbate gum issues. Engage in activities that help you manage stress, such as exercise, mindfulness, and spending time with loved ones.
Avoid Tobacco Products
Smoking and tobacco use are detrimental to gum health. These habits reduce blood flow to the gums, impairing their ability to heal and fight infection. Quitting tobacco can have a positive impact on your gum health and overall well-being.
Educate Yourself
Stay informed about gum health and oral hygiene practices. The more you know, the better equipped you’ll be to make informed decisions about your oral care routine.
Embracing Long-Term Benefits
Investing in gum health offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond a dazzling smile. By nurturing healthy gums, you’re taking proactive steps to prevent gum disease, tooth loss, and potential systemic health complications. Remember that gum health is an integral part of your overall well-being, and maintaining it requires consistent effort and dedication.
Conclusion
Gum health is a fundamental component of overall oral hygiene and plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall health. Neglecting gum health can lead to a range of issues, from gingivitis and periodontitis to systemic health implications. By adopting effective oral hygiene practices, maintaining a balanced diet, and making regular dental visits, you can significantly improve and preserve your gum health. Remember, healthy gums contribute not only to a beautiful smile but also to your overall well-being.