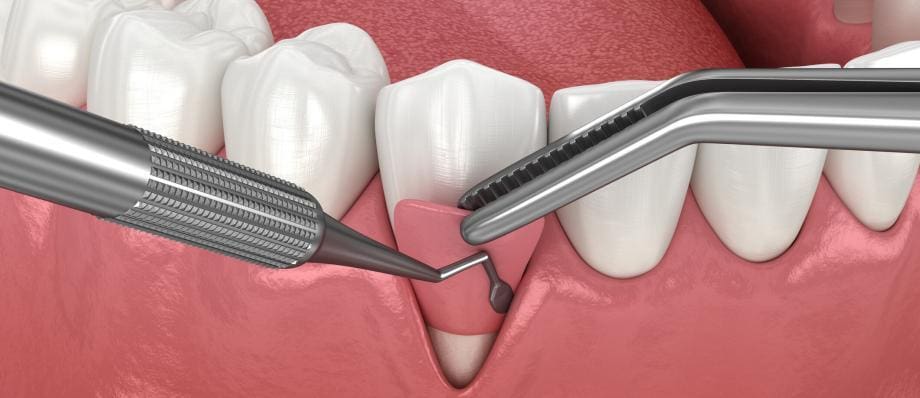
Gum grafting, also known as periodontal plastic surgery, is a dental procedure that involves taking gum tissue from one area of the mouth and placing it in an area where the gum tissue has receded or is deficient. Gum grafting is typically used to treat gum recession, which is a common condition that can cause tooth sensitivity, root exposure, and even tooth loss if left untreated.
In this article, we will discuss what gum grafting is, why it is performed, the different types of gum graft procedures, the benefits and risks of gum graft, and what to expect before, during, and after the procedure.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is gum grafting?
Gum grafting is a surgical procedure that involves taking tissue from one part of the mouth, such as the palate, and attaching it to the area of the gum that is deficient. The purpose of gum graft is to improve the health and appearance of the gums, as well as to prevent further gum recession and tooth loss.
Why is gum graft performed?
Gum grafting is typically performed to treat gum recession, which is a common condition that occurs when the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth, exposing the roots of the teeth. Gum recession can be caused by a variety of factors, including gum disease, aggressive brushing or flossing, genetics, and hormonal changes.
Gum recession can cause a number of dental problems, including tooth sensitivity, root decay, and even tooth loss if left untreated. Gum graft can help to prevent these problems and improve the appearance of the gums.
Types of gum grafting procedures
There are several different types of gum grafting procedures, including:
- Connective tissue grafts
- Free gingival grafts
- Pedicle grafts
Connective tissue grafts
This is the most common type of gum graft procedure. It involves taking tissue from underneath a flap of skin on the roof of the mouth and attaching it to the area of the gum that is deficient.
Free gingival grafts
This procedure involves taking tissue directly from the roof of the mouth and attaching it to the area of the gum that is deficient.
Pedicle grafts
This procedure involves taking tissue from an adjacent area of the gum and pulling it over to cover the area of the gum that is deficient.
The type of gum graft procedure used will depend on the severity and location of the gum recession.
Benefits of gum grafting
Gum grafting can provide several benefits, including:
- Improved oral health
- Appearance
- Comfort
Improved oral health
Gum graft can help to prevent tooth sensitivity, root decay, and tooth loss by covering the exposed roots of the teeth and preventing further gum recession.
Appearance
Gum grafting can improve the appearance of the gums by covering areas of recession and creating a more even gum line.
Comfort
Gum graft can reduce tooth sensitivity and discomfort caused by exposed roots.
Risks of gum graft
Like any surgical procedure, gum grafting does carry some risks, including:
- Pain and discomfort
- Swelling
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Poor outcome
Pain and discomfort
Patients may experience pain and discomfort in the treated area for several days after the procedure.
Swelling
Swelling and bruising are common after gum graft, and can last for several days.
Bleeding
Patients may experience some bleeding in the treated area for several days after the procedure.
Infection
There is a risk of infection with any surgical procedure, including gum grafting.
Poor outcome
In some cases, the graft may not take or may not provide the desired result.
What to expect before, during, and after gum grafting
- Before the procedure
- During the procedure
- After the procedure
Before the procedure
Before gum grafting, the dentist will perform a thorough examination of the teeth and gums, and may take X-rays to evaluate the extent of the gum recession. Patients will also be given instructions on how to prepare for the procedure, which may include avoiding certain foods and medications.
During the procedure
Gum grafting is typically performed under local anesthesia, which means that patients will be awake but will not feel any pain during the procedure. The dentist will make a small incision in the gum tissue and will then place the graft over the area of recession. The graft will be secured in place with sutures, and patients may be given a protective dressing to wear over the area.
After the procedure
Patients will typically need to rest for a few days after gum grafting, and may need to avoid certain foods and activities during this time. Pain and discomfort can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications, and patients should avoid brushing or flossing the treated area until it has healed. Patients will also need to attend follow-up appointments with their dentist to monitor the healing process and ensure that the graft is successful.
Conclusion
Gum grafting is a common dental procedure that can provide significant benefits for patients with gum recession. While it does carry some risks, the benefits of gum graft can include improved oral health, improved appearance, and improved comfort. If you are experiencing gum recession, talk to your dentist about whether gum grafting may be right for you.
It’s important to note that gum grafting is not always necessary for every case of gum recession. In some cases, a change in oral hygiene habits or a professional cleaning may be enough to halt the progression of gum recession. However, if left untreated, gum recession can lead to more serious dental problems, such as tooth loss or gum disease, so it’s important to address any concerns with your dentist.
Additionally, while gum graft can provide significant benefits, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The type of gum grafting procedure used, as well as the success of the graft, will depend on a variety of factors, including the extent of the gum recession, the location of the recession, and the patient’s overall oral health.
If you are considering gum graft, it’s important to discuss the procedure with your dentist in detail and to ask any questions you may have. Your dentist can provide you with information on the risks and benefits of the procedure, as well as what to expect before, during, and after the procedure. With proper care and follow-up, gum grafting can be an effective way to improve the health and appearance of your gums and protect your teeth from further damage.