Dental implants have revolutionized modern dentistry, offering a durable and effective solution for replacing missing teeth. One critical factor influencing the success of dental implants is the surface characteristics of the implant. The surface of dental implants plays a crucial role in promoting osseointegration, stability, and long-term success. In this article, we delve into the significance of dental implant surfaces, exploring their impact on implant performance and patient outcomes.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Dental Implant Surfaces
Dental implants are typically made of biocompatible materials such as titanium or its alloys. These materials are chosen for their excellent mechanical properties and ability to integrate with the surrounding bone tissue. However, the surface properties of implants can vary significantly, influencing their biological response within the oral environment.
The surface of a dental implant can be modified through various processes to enhance its characteristics. These modifications may include altering the topography, chemistry, or roughness of the implant surface. Common techniques for modifying implant surfaces include sandblasting, acid etching, anodization, and coating with bioactive materials.
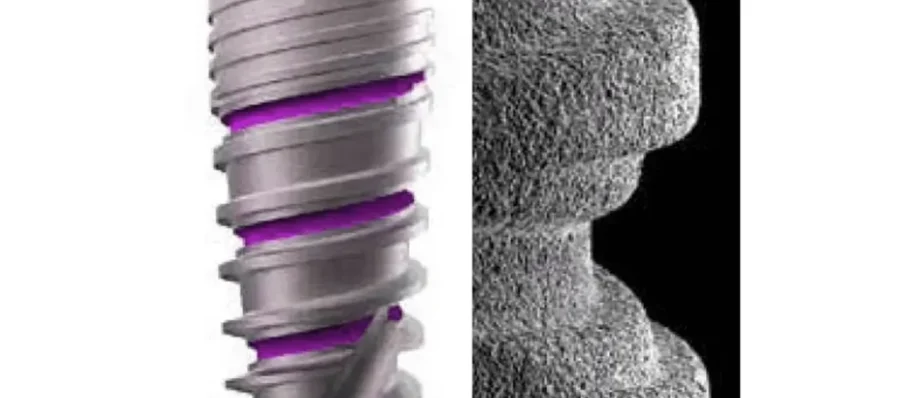
Importance of Surface Topography
The topography of the implant surface refers to its microscopic features, such as roughness, texture, and porosity. Research has shown that surface topography plays a crucial role in promoting osseointegration, the process by which the implant fuses with the surrounding bone.
A roughened surface enhances the implant’s mechanical interlocking with the bone, providing greater stability during the healing process. Microscopic irregularities on the implant surface create more surface area for bone cells to attach and proliferate, facilitating faster osseointegration and reducing healing times.
Furthermore, the roughness of the implant surface can influence the formation of a biological seal around the implant, known as the soft tissue interface. A properly designed surface topography promotes the formation of a stable soft tissue seal, reducing the risk of bacterial infiltration and peri-implant inflammation.
Dental Implant Surface Chemistry and Bioactivity
In addition to topography, the chemistry of the implant surface also plays a significant role in determining its biological response. Surface modifications can alter the chemical composition of the implant, making it more conducive to osseointegration.
One approach to enhancing surface chemistry is through the incorporation of bioactive materials or coatings. These materials, such as hydroxyapatite or calcium phosphate, mimic the composition of natural bone and stimulate bone formation around the implant. Bioactive coatings promote early bone apposition and improve the long-term stability of dental implants.
Furthermore, surface modifications can influence the release of signaling molecules and growth factors that regulate the bone healing process. By controlling the release kinetics of these molecules, implant surfaces can actively modulate the surrounding tissue response, promoting faster and more predictable bone regeneration.
Impact on Clinical Outcomes
The surface characteristics of dental implants have a direct impact on clinical outcomes, including implant survival rates, success rates, and patient satisfaction. Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the superior performance of implants with optimized surface properties compared to conventional smooth implants.
A systematic review published in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology found that roughened implant surfaces significantly improved osseointegration and clinical outcomes compared to machined surfaces. The review concluded that rough surface implants exhibited higher success rates and lower rates of peri-implantitis, a common inflammatory complication associated with dental implants.
Furthermore, long-term follow-up studies have shown that implants with bioactive coatings or surface modifications maintain their stability and function over extended periods. Enhanced osseointegration and soft tissue integration contribute to reduced bone loss around the implant and lower incidence of peri-implant complications, ensuring predictable long-term outcomes for patients.
Future Directions and Innovations
As the field of implant dentistry continues to evolve, researchers and manufacturers are exploring new strategies to further improve the surface characteristics of dental implants. Emerging technologies, such as laser surface modification and additive manufacturing, offer precise control over implant topography and chemistry, allowing for custom-designed surfaces tailored to individual patient needs.
Moreover, the integration of biomimetic materials and growth factor delivery systems holds promise for enhancing the bioactivity of implant surfaces. By mimicking the natural composition and structure of bone tissue, these advanced surfaces stimulate more robust bone regeneration and accelerate the healing process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the surface characteristics of dental implants play a crucial role in determining their biological response, stability, and long-term success. Surface topography, chemistry, and bioactivity influence the process of osseointegration and soft tissue integration, ultimately impacting clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction.
By optimizing implant surfaces through advanced surface modifications and coatings, clinicians can enhance the performance and longevity of dental implants, providing patients with durable and functional tooth replacement solutions. Continued research and innovation in implant surface engineering will further advance the field of implant dentistry, offering new possibilities for improving patient care and treatment outcomes.