Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is a condition that occurs when the salivary glands in the mouth fail to produce enough saliva to keep the mouth moist. Saliva is essential for maintaining good oral health and helps to protect the teeth from decay, aids in digestion, and keeps the mouth lubricated. When there is not enough saliva, it can cause a variety of uncomfortable symptoms and increase the risk of developing oral health problems.
Causes of Dry Mouth
There are several causes of dry mouth, including medication use, medical conditions, and lifestyle factors. Some of the most common causes include:
- Medication Use
- Medical Conditions
- Aging
- Lifestyle Factors
Medication Use
Many medications can cause dry mouth as a side effect. This includes over-the-counter medications such as antihistamines and decongestants, as well as prescription medications for conditions such as high blood pressure, depression, and anxiety.
Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can cause dry mouth, including diabetes, autoimmune diseases such as Sjogren’s syndrome, HIV/AIDS, and Parkinson’s disease.
Aging
Many elderly people suffer from dry mouth due to aging. Factors contributing to dry mouth include the use of certain medications, changes in the body’s ability to digest medications, poor nutrition, and long-term health problems. Chemotherapy drugs can change the nature and amount of saliva production. This change may be temporary and the normal flow of saliva production will return to normal after the completion of the treatment period. Radiation therapy in the head and neck damages the salivary glands and causes a significant decrease in saliva production. This problem may be temporary or permanent depending on the amount of radiation therapy and the treated area.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle factors can also contribute to dry mouth, such as smoking, alcohol use, and breathing through the mouth instead of the nose.
Symptoms of Dry Mouth
The symptoms of dry mouth can vary in severity, but they can be very uncomfortable and impact the quality of life. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- A dry, sticky feeling in the mouth
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing
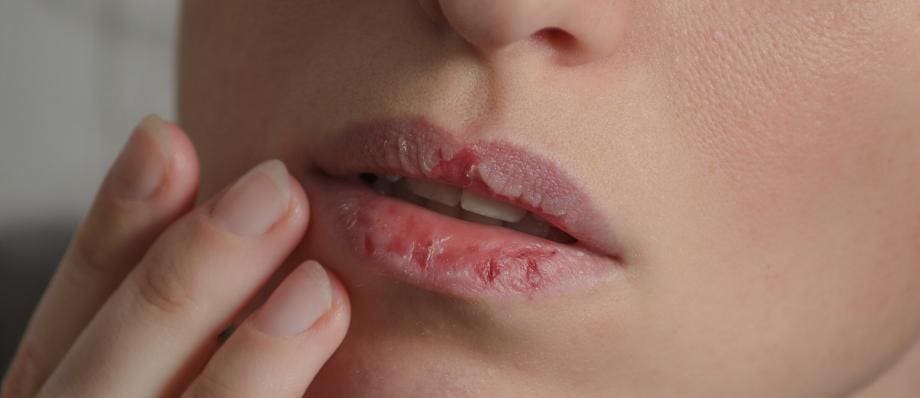
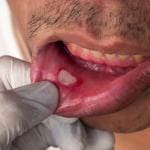
- Cracked lips or sores in the mouth
- Bad breath
- Changes in taste
- A sore throat or hoarseness
- Increased risk of tooth decay and gum disease
- Difficulty in wearing dentures
Treatment for Dry Mouth
The treatment for dry mouth depends on the underlying cause of the condition. If dry mouth is caused by medication use, switching to a different medication or adjusting the dosage may help alleviate symptoms. In cases where dry mouth is caused by a medical condition, treating the underlying condition may help improve symptoms.
There are also several lifestyle changes and home remedies that can help alleviate symptoms of dry mouth, including:
- Drinking plenty of water throughout the day
- Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free candy to stimulate saliva production
- Avoiding tobacco and alcohol use
- Using a humidifier in the bedroom to keep the air moist
- Brushing and flossing regularly to prevent tooth decay and gum disease
In some cases, a doctor or dentist may recommend using artificial saliva products, which are designed to mimic the natural saliva in the mouth and help alleviate symptoms of dry mouth.
Complications of Dry Mouth
Without adequate saliva production, the risk of developing oral health problems such as tooth decay and gum disease increases. Saliva helps to wash away food particles and bacteria in the mouth, and without it, these particles can stick to the teeth and gums, causing plaque buildup and cavities.
Dry mouth can also cause problems with digestion, as saliva plays a key role in breaking down food in the mouth and beginning the digestive process. This can lead to issues such as difficulty swallowing, indigestion, and acid reflux.
- Plaque buildup leading to tooth decay and gum disease
- Burning sensation in the mouth
- Fungal infection or thrush in the mouth
- Rough or cracked skin at the corners of the mouth or chapped lips
- Difficulty with chewing and swallowing leading to poor nutrition
In addition, dry mouth can impact the overall quality of life, causing discomfort and difficulty speaking or eating.
Preventing Dry Mouth
While some causes of dry mouth, such as medication use or medical conditions, cannot be prevented, there are several lifestyle changes that can help reduce the risk of developing the condition. These include:
- Drinking plenty of water throughout the day
- Avoiding tobacco and alcohol use
- Using a humidifier in the bedroom to keep the air moist
- Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free candy to stimulate saliva production
- Eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, which can help stimulate saliva production
It is also important to maintain good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing and flossing
regularly and visiting the dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings. This can help prevent tooth decay and gum disease, which can exacerbate the symptoms of dry mouth.
When to See a Doctor
If you are experiencing symptoms of dry mouth, it is important to speak with a doctor or dentist to determine the underlying cause of the condition. In some cases, dry mouth can be a symptom of a more serious medical condition, so it is important to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen.
If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms along with dry mouth, seek medical attention immediately:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Severe pain in the mouth or throat
- Persistent dry mouth despite making lifestyle changes or using artificial saliva products
- Swelling or lumps in the mouth or throat
These symptoms could indicate a more serious underlying condition, such as oral cancer, and require prompt medical attention.
Conclusion
Dry mouth is a common condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, including medication use, medical conditions, and lifestyle factors. While it can be uncomfortable and impact the quality of life, there are several treatment options and lifestyle changes that can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of developing complications such as tooth decay and gum disease. If you are experiencing symptoms of dry mouth, speak with a doctor or dentist to determine the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan.