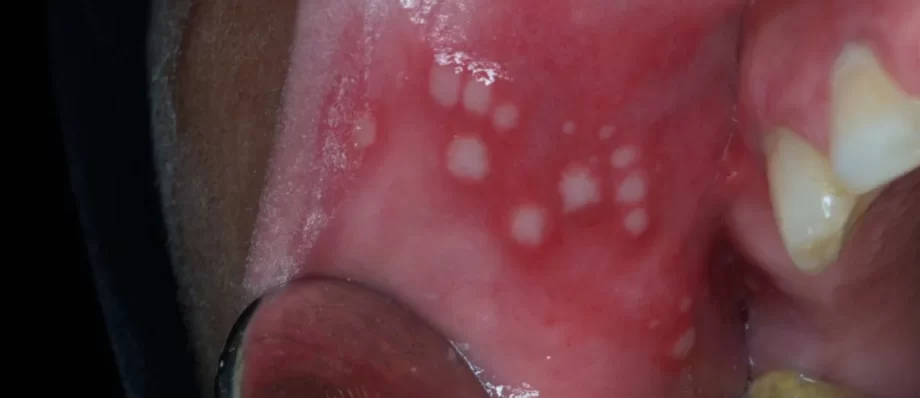
Behchet’s disease, named after the Turkish dermatologist Hulusi Behchet who first described it in 1937, is a chronic and complex autoimmune condition characterized by recurring inflammation throughout the body. This condition primarily affects blood vessels and causes a wide range of symptoms that can be challenging to diagnose and manage.
Table of Contents
ToggleSymptoms and Manifestations
Behchet’s disease exhibits a variety of symptoms that can affect multiple systems within the body. Its hallmark symptoms include:
- Oral Ulcers
- Genital Ulcers
- Skin Lesions
- Eye Inflammation
- Arthritis
- Gastrointestinal Complications
- Central Nervous System Involvement
Oral Ulcers
Painful sores develop in the mouth and canker sores appear on the lips and tongue, usually as the initial sign of the disease.
Genital Ulcers
Similar painful ulcers can develop on the genitals, causing discomfort and distress.
Skin Lesions
Various skin manifestations, such as acne-like nodules, erythema nodosum (reddish lumps), and folliculitis (inflamed hair follicles), are common in Behchet’s.
Eye Inflammation
Ocular involvement is prevalent and can lead to uveitis, retinal vasculitis, and in severe cases, blindness.
Arthritis
Joint pain and swelling, resembling symptoms of arthritis, are frequent in Behchet’s disease.
Gastrointestinal Complications
Abdominal pain, diarrhea, and bleeding from the gut due to ulcers can occur, impacting digestive health.
Central Nervous System Involvement
Less common but potentially serious, Behchet’s disease may lead to neurological complications like headaches, seizures, and inflammation of the brain and spinal cord.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Behchet’s disease remains elusive. However, it’s believed to be an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its tissues, leading to inflammation. Several factors may contribute to its development:
- Genetics
- Environmental Triggers
Genetics
There’s a genetic predisposition, as certain ethnic groups, particularly those of Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and Asian descent, are more susceptible to Behchet’s disease.
Environmental Triggers
Infections, bacterial or viral, might trigger the immune system in genetically susceptible individuals, leading to the development of Behchet’s disease.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Behchet’s disease can be challenging due to the diverse range of symptoms and the absence of a specific test. Physicians typically rely on a combination of medical history, clinical examination, and ruling out other conditions that mimic its symptoms.
Treatment and Management
The management of Behchet’s disease aims at reducing inflammation, controlling symptoms, and preventing complications. Treatment usually involves a multidisciplinary approach:
- Medications
- Topical Treatments
- Eye Care
- Pain Management
Medications
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and immunosuppressive drugs like azathioprine, methotrexate, or biologics may be prescribed to manage inflammation.
Topical Treatments
Topical steroids or mouth rinses can alleviate oral and genital ulcers.
Eye Care
Ophthalmologic involvement necessitates specialized treatment to prevent vision loss, including corticosteroid eye drops or injections.
Pain Management
Pain medications or other interventions may be necessary to address joint pain or neuropathic symptoms.
Living with Behchet’s Disease
Living with Behchet’s disease can be challenging due to its unpredictable nature. Patients often experience periods of remission and flares, where symptoms worsen. Self-care and lifestyle adjustments play a vital role in managing this condition:
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Stress Management
- Regular Follow-ups
Healthy Lifestyle
A balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate rest can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Stress Management
Stress reduction techniques, such as meditation or counseling, may help in minimizing the frequency and severity of flares.
Regular Follow-ups
Consistent monitoring and follow-ups with healthcare providers are crucial to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Research and Future Prospects
Ongoing research aims to understand the underlying mechanisms of Behchet’s disease better and develop more targeted therapies. Genetic studies, immunological research, and clinical trials are underway to explore new treatment options and improve outcomes for individuals affected by this condition.
Recent Advances and Supportive Therapies
Recent medical advancements have brought forth promising avenues for managing Behchet’s disease. Among these are:
- Biologic Therapies
- Vascular Interventions
- Supportive Therapies
Biologic Therapies
Biologic medications targeting specific immune system components, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or interleukin inhibitors, have shown efficacy in reducing inflammation and controlling symptoms in some individuals who are resistant to conventional therapies.
Vascular Interventions
In severe cases where blood vessel involvement is critical, interventions like angioplasty or stenting may be considered to address vessel narrowing or blockages.
Supportive Therapies
Supportive care, including physical therapy for joint pain, nutritional counseling for gastrointestinal symptoms, and psychological support, plays a vital role in enhancing the overall well-being of individuals with Behchet’s disease.
Conclusion
Behchet’s disease is a complex autoimmune condition characterized by recurring inflammation that affects various organs and systems in the body. While there’s no cure, early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle modifications can significantly improve the quality of life for those living with this challenging condition. Continued research efforts offer hope for better understanding, management, and treatment of Behchet’s disease in the future.