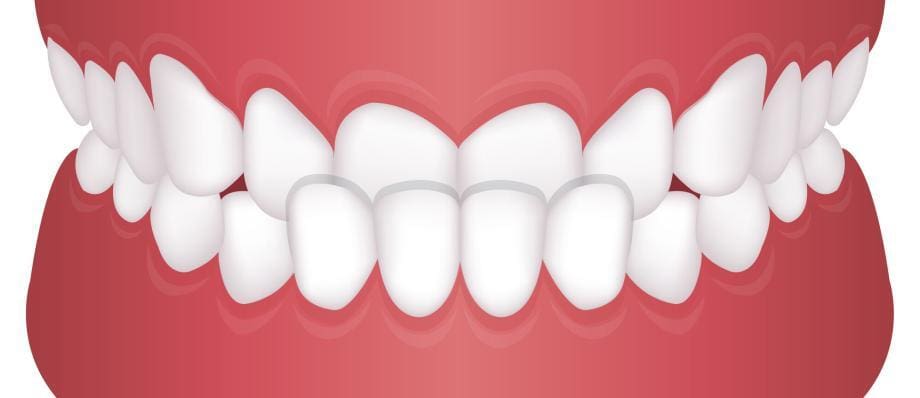
An underbite, also known as a Class III malocclusion, is a dental condition where the lower teeth and jaw protrude beyond the upper teeth and jaw, resulting in an abnormal bite alignment. This condition can affect both children and adults and may lead to various dental and skeletal issues if left untreated. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options for underbites.
Table of Contents
ToggleCauses of Underbite
Underbites can develop due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some common causes include:
- Genetics
- Abnormal Jaw Growth
- Thumb-Sucking or Prolonged Pacifier Use
- Childhood Oral Habits
- Injury or Trauma
- Cleft Lip and Palate
Genetics
In many cases, an underbite is inherited from one or both parents. If a family member has an underbite, there is a higher likelihood of the condition being passed on to future generations.
Abnormal Jaw Growth
Irregular growth of the lower jaw can lead to an underbite. This may be caused by genetic factors or environmental influences during development.
Thumb-Sucking or Prolonged Pacifier Use
Sustained habits like thumb-sucking or reliance on a pacifier can impact the alignment of the teeth and jaw, potentially contributing to the development of an underbite.
Childhood Oral Habits
Certain childhood habits, such as tongue thrusting or prolonged bottle-feeding, can affect jaw and tooth alignment.
Injury or Trauma
Severe injury or trauma to the jaw region can disrupt the normal alignment of the teeth and jaw, resulting in an underbite.
Cleft Lip and Palate
Individuals born with a cleft lip or palate may experience an underbite due to the irregular development of the jaw and surrounding structures.
Symptoms of Underbite
Recognizing the symptoms of an underbite is essential for early detection and intervention. Some common signs include:
- Visible Protrusion
- Misaligned Bite
- Difficulty Chewing and Biting
- Speech Problems
- Breathing Issues
- Facial Asymmetry
Visible Protrusion
The most apparent symptom is the noticeable protrusion of the lower jaw beyond the upper jaw when the mouth is closed.
Misaligned Bite
The upper and lower teeth may not fit together correctly when the jaw is closed, leading to an abnormal bite pattern.
Difficulty Chewing and Biting
An underbite can hinder proper chewing and biting, leading to issues with food digestion.
Speech Problems
Some individuals with underbites may experience speech difficulties due to the misalignment of the jaw and teeth.
Breathing Issues
In severe cases, an underbite can cause breathing problems, especially during sleep.
Facial Asymmetry
An underbite can sometimes result in facial asymmetry, with one side of the face appearing more prominent than the other.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
If an underbite is suspected, it is essential to consult a qualified orthodontist or dentist for a comprehensive evaluation. The diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical and Dental History
- Physical Examination
- X-rays and Imaging
Medical and Dental History
The healthcare professional will inquire about the patient’s medical and dental history, as well as any family history of dental conditions.
Physical Examination
The orthodontist will conduct a thorough physical examination of the patient’s teeth, jaw, and facial structure.
X-rays and Imaging
X-rays and other imaging techniques, such as panoramic radiographs, may be used to assess the severity of the underbite and identify any underlying issues.
Treatment Options
The appropriate treatment for an underbite depends on its severity, the age of the patient, and other individual factors. Several treatment options are available, including:
- Orthodontic Treatment
- Jaw Surgery
- Reverse Pull Face Mask
- Chin Cap
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
Orthodontic Treatment
Mild to moderate underbites can often be corrected with orthodontic appliances such as braces or clear aligners. These appliances gradually move the teeth into the correct position over time.
Jaw Surgery
Severe underbites that result from significant jaw misalignment may require corrective jaw surgery, also known as orthognathic surgery. This procedure involves repositioning the jawbones to achieve proper alignment.
Reverse Pull Face Mask
In growing children, a reverse pull face mask may be used to guide the growth of the upper jaw, helping to correct the underbite.
Chin Cap
In some cases, a chin cap can be used to restrict the growth of the lower jaw, aiding in aligning the upper and lower jaws correctly.
Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
Individuals with an underbite resulting from a cleft lip or palate may require surgical intervention to correct the underlying condition.
Prevention and Early Intervention
While some underbites are genetically determined and cannot be prevented, there are steps that parents and caregivers can take to minimize the risk or detect the condition early:
- Regular Dental Check-ups
- Thumb-Sucking and Pacifier Habits
- Oral Habits
- Orthodontic Evaluation
Regular Dental Check-ups
Schedule regular dental check-ups for your child from an early age. Dentists can identify potential bite alignment issues and provide appropriate guidance.
Thumb-Sucking and Pacifier Habits
Encourage your child to discontinue thumb-sucking or pacifier use by the age of three. Prolonged habits can impact dental development.
Oral Habits
Monitor and discourage any oral habits that may negatively affect dental and jaw development, such as tongue thrusting.
Orthodontic Evaluation
If you suspect an underbite or notice any signs of misalignment, seek an orthodontic evaluation at an early age. Early detection allows for more effective and less invasive treatment.
Living with an Underbite: Coping and Support
Living with an underbite can present challenges, but there are coping strategies and support systems available to help individuals navigate their journey towards treatment and improved oral health.
- Self-Education
- Seek Professional Guidance
- Emotional Support
- Positive Self-Image
- Speech and Communication
- Nutrition and Oral Care
- Early Intervention for Children
Self-Education
Understanding the nature of the condition and its treatment options is essential. Empowering oneself with knowledge about underbites can alleviate anxiety and fear surrounding the condition. Books, articles, and reliable online resources can provide valuable information.
Seek Professional Guidance
Consult with an experienced orthodontist or dentist who specializes in underbite correction. They can guide you through the available treatment options and develop a personalized plan for your specific needs.
Emotional Support
Coping with a dental condition can be emotionally challenging. Seek support from family, friends, or a support group. Connecting with others who have undergone similar experiences can provide a sense of belonging and understanding.
Positive Self-Image
Emphasize your other unique qualities and talents beyond your dental condition. Cultivate self-confidence and focus on your strengths.
Speech and Communication
If an underbite affects speech, consider speech therapy to improve communication skills. A speech therapist can offer techniques to overcome speech difficulties and build confidence in communication.
Nutrition and Oral Care
Focus on maintaining good oral hygiene and a balanced diet. Brush and floss regularly to prevent dental issues that may exacerbate the underbite. A well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports overall oral health.
Early Intervention for Children
If your child has an underbite, early intervention is crucial. Seeking treatment during childhood can reduce the severity of the condition and may eliminate the need for more invasive treatments later in life.
Potential Complications of Untreated Underbite
Leaving an underbite untreated can lead to various complications, including:
- Dental Issues
- Speech Problems
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
- Breathing Problems
- Facial Aesthetics
Dental Issues
An underbite can cause excessive wear and tear on the front teeth, leading to enamel erosion, chipping, or cracking.
Speech Problems
The misalignment of the jaws and teeth can affect speech clarity, resulting in difficulties with pronunciation and articulation.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
An underbite can strain the jaw joints, leading to TMJ disorders, which may cause jaw pain, headaches, and difficulty opening and closing the mouth.
Breathing Problems
In severe cases, an underbite can impact the airway, causing breathing difficulties, especially during sleep.
Facial Aesthetics
An untreated underbite can result in facial asymmetry, affecting the overall appearance and self-confidence of the individual.
Conclusion
An underbite is a dental condition that should not be ignored, as it can lead to dental, skeletal, and psychological complications if left untreated. Recognizing the symptoms early, seeking professional evaluation, and adhering to an appropriate treatment plan can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with underbites. Remember that underbites can be effectively treated through various orthodontic and surgical options, and support from family, friends, and qualified healthcare professionals can make the journey more manageable.
If you or your child exhibit signs of an underbite, do not hesitate to consult with a qualified orthodontist or dentist to discuss evaluation and treatment options. By taking proactive steps, you can address the condition early, promote optimal oral health, and improve overall well-being. Remember that each individual’s case is unique, and personalized treatment plans are vital for achieving the best outcomes. With the right care, support, and professional guidance, living with an underbite can become a manageable aspect of life, ultimately leading to a healthy and confident smile.