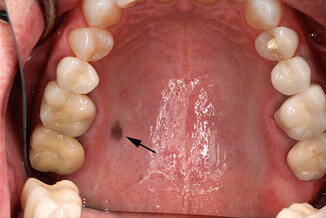
Oral nevi, also known as oral melanocytic nevi, represent a fascinating and relatively uncommon group of lesions that occur in the oral cavity. These pigmented lesions may resemble melanoma, a potentially deadly form of skin cancer, but they are typically benign. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the world of oral nevi, exploring their characteristics, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and their significance in oral health.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Oral Nevi
Oral nevi are benign melanocytic lesions that occur in the oral cavity. They are composed of melanocytes, which are pigment-producing cells that give color to the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes, including the mouth. Oral nevi can manifest in various forms, including flat, elevated, or nodular lesions, and their coloration can range from brown to black. These lesions are primarily found on the buccal mucosa (inner cheek), followed by the palate, gingiva (gums), and tongue.
Characteristics of Oral Nevi
- Coloration
- Shape and Size
- Texture
- Borders
Coloration
Oral nevi typically appear brown or black due to the presence of melanin. The color may vary depending on the concentration of melanin and the depth of the lesion.
Shape and Size
These lesions can vary in shape, ranging from small, round macules (flat spots) to larger, irregularly shaped patches. Their size can also vary, with some lesions being less than 1 cm and others exceeding 2 cm in diameter.
Texture
The texture of oral nevi may range from smooth to slightly raised or even nodular. Some nevi may have a velvety appearance.
Borders
Benign oral nevi usually have well-defined borders that distinguish them from more concerning lesions like melanoma, which may exhibit irregular or blurred borders.
Causes of Oral Nevi
The exact causes of oral nevi remain unclear, but there are several factors that may contribute to their development:
- Genetic Predisposition
- Sun Exposure
- Hormonal Changes
- Inflammatory Factors
Genetic Predisposition
There is evidence to suggest that genetics plays a role in the development of oral nevi. Individuals with a family history of nevi or melanoma may have a higher risk.
Sun Exposure
While sunlight exposure is a well-known risk factor for cutaneous (skin) nevi, it is less clear whether it plays a significant role in the development of oral nevi due to the limited sunlight exposure in the oral cavity.
Hormonal Changes
Some studies have indicated that hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy, may influence the development or darkening of oral nevi.
Inflammatory Factors
Chronic irritation or inflammation of the oral mucosa may be associated with the formation of oral nevi in some cases.
Diagnosis of Oral Nevi
Diagnosing oral nevi typically involves a combination of clinical examination and, in some cases, biopsy. Here’s how the diagnosis process unfolds:
- Clinical Examination
- Dermatoscopic Evaluation
- Biopsy
Clinical Examination
A thorough examination of the oral cavity by a dentist or oral healthcare professional is often the first step in diagnosing oral nevi. They will assess the lesion’s size, color, shape, and texture.
Dermatoscopic Evaluation
In some instances, dermatoscopy (a non-invasive imaging technique) may be used to examine the lesion more closely. Dermatoscopy can reveal specific patterns that help differentiate between benign nevi and potentially malignant lesions.
Biopsy
When there is uncertainty about the nature of the lesion or if it shows any suspicious features, a biopsy may be performed. During a biopsy, a small sample of the lesion is removed and sent to a pathology lab for microscopic examination. This allows for a definitive diagnosis and rules out the possibility of malignancy.
Types of Oral Nevi
There are several types of oral nevi, each with distinct characteristics:
- Intramucosal Nevi
- Junctional Nevi
- Compound Nevi
- Dermal Nevi
Intramucosal Nevi
These nevi are confined to the mucosal (inner) layer of the oral cavity. They are typically brown or black and may have a flat or slightly raised appearance.
Junctional Nevi
Junctional nevi occur at the junction between the epithelium (surface layer) and the connective tissue. They often appear as brown to black macules and are typically flat.
Compound Nevi
Compound nevi involve both the epithelial and connective tissue components of the oral mucosa. They may present as slightly raised, brown to black lesions.
Dermal Nevi
Dermal nevi are predominantly located in the connective tissue layer beneath the oral mucosa. They may appear as elevated or nodular lesions.
Treatment of Oral Nevi
The treatment of oral nevi primarily depends on their characteristics, size, location, and the patient’s preference. Most oral nevi are benign and do not require treatment beyond regular monitoring. However, there are treatment options available for cosmetic or functional reasons:
- Excision
- Laser Therapy
- Cryotherapy
- Observation
Excision
Surgical excision may be considered for large or bothersome nevi. This procedure involves removing the lesion along with a margin of healthy tissue. It is typically performed under local anesthesia, and the excised tissue is sent for histopathological examination to confirm its benign nature.
Laser Therapy
Lasers can be used to treat pigmented lesions, including oral nevi. Laser therapy aims to break down the melanin in the nevus, leading to its gradual fading. Multiple sessions may be required.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing the nevus with liquid nitrogen. This can be effective for small, superficial lesions.
Observation
In many cases, especially when oral nevi are small and pose no functional or cosmetic concerns, a “watch and wait” approach is recommended. Regular follow-up appointments with an oral healthcare provider are essential to monitor any changes.
Significance of Oral Nevi in Oral Health
Oral nevi, though typically benign, are significant in the field of oral health for several reasons:
- Differential Diagnosis
- Cosmetic Concerns
- Psychological Impact
- Oral Cancer Awareness
Differential Diagnosis
Distinguishing between benign oral nevi and potentially malignant lesions like melanoma is crucial. Proper diagnosis ensures appropriate treatment and helps avoid unnecessary anxiety for patients.
Cosmetic Concerns
Depending on their size and location, oral nevi can be a source of cosmetic concern for some individuals. Treatment options are available to address these concerns.
Psychological Impact
The presence of a pigmented lesion in the oral cavity can cause anxiety or distress in patients. Education and counseling are important to alleviate such concerns.
Oral Cancer Awareness
Regular oral health check-ups that include the examination of oral nevi contribute to early detection and management of oral cancer, which is crucial for better outcomes.
Conclusion
Oral nevi are intriguing benign pigmented lesions that can be found in the oral cavity. While they are typically harmless, their resemblance to melanoma warrants proper diagnosis and monitoring by oral healthcare professionals. Understanding their characteristics, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. With appropriate care and vigilance, individuals with oral nevi can maintain good oral health and peace of mind.