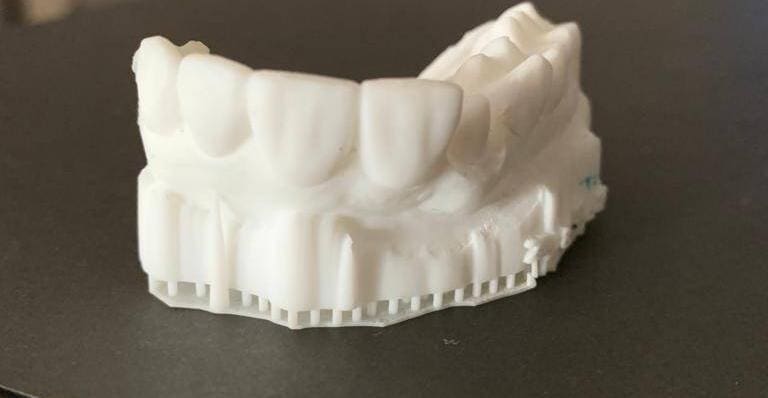
The field of dentistry has witnessed a revolutionary transformation with the advent of 3D printing technology. 3D printers, also known as additive manufacturing devices, have gained significant traction in various industries, including healthcare. In dentistry, 3D printing has emerged as a powerful tool, enabling the creation of highly precise and patient-specific dental implants, prosthetics, surgical guides, and models. This article explores the impact of 3D printers and 3D printing in dentistry, discussing the technology, applications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding 3D Printing Technology
3D printing, also referred to as additive manufacturing, is a process that creates three-dimensional objects from a digital model by layering material sequentially. The technology involves several key steps:
- Digital Design
- Slicing
- Printing
- Curing and Solidifying
- Post-Processing
Digital Design
A 3D model of the object is created using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
Slicing
The digital model is sliced into thin horizontal cross-sections using slicing software, generating a set of 2D images that will guide the 3D printer.
Printing
The 3D printer follows the instructions from the sliced model, layering the chosen material (usually plastics, resins, metals, or ceramics) to build the object layer by layer.
Curing and Solidifying
Depending on the material used, curing processes like UV light exposure or heating solidify and harden the layers.
Post-Processing
After printing, the object may undergo post-processing steps such as cleaning, curing, polishing, or painting to achieve the desired finish and functionality.
Applications of 3D Printing in Dentistry
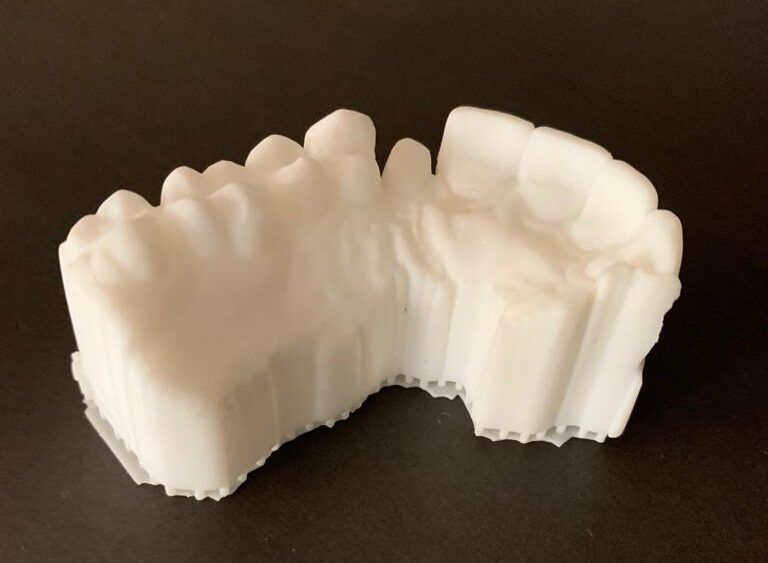

- Dental Models and Prototypes
- Dental Implants
- Crowns, Bridges, and Dentures
- Surgical Guides
- Orthodontic Devices
Dental Models and Prototypes
3D printing allows for the precise and efficient creation of dental models and prototypes, providing dentists and dental technicians with a tangible replica of a patient’s oral anatomy. These models aid in treatment planning, surgical simulations, and the fabrication of various dental devices.
Dental Implants
Customized dental implants can be designed and fabricated using 3D printing technology. These implants are tailored to fit a patient’s unique anatomy, enhancing implant success rates and reducing surgery time.
Crowns, Bridges, and Dentures
3D printing enables the fabrication of crowns, bridges, and dentures with exceptional precision and accuracy. The patient’s specific dental anatomy is used to create custom-fitted prosthetic devices, improving comfort and functionality.
Surgical Guides
3D printing allows for the production of surgical guides, providing precise guides for dental implant placement and other surgical procedures. This improves surgical accuracy, reduces operating time, and minimizes complications.
Orthodontic Devices
Customized orthodontic devices like braces and aligners can be manufactured using 3D printing, allowing for a more tailored and efficient orthodontic treatment plan.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Dentistry
- Personalized Treatment
- Increased Efficiency
- Cost-Effectiveness
- Enhanced Precision and Quality
Personalized Treatment
One of the significant benefits of 3D printing in dentistry is the ability to provide personalized treatment for each patient. The technology allows for the creation of dental devices and prosthetics that perfectly match an individual’s unique oral anatomy.
Increased Efficiency
3D printing significantly improves the efficiency of the dental fabrication process. Dental labs can produce highly accurate dental devices in a shorter amount of time compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in a 3D printer and materials may seem high, the overall cost of producing custom dental devices can be reduced in the long run due to the efficiency and material savings offered by 3D printing.
Enhanced Precision and Quality
The precision and quality achievable with 3D printing are exceptional. The digital design and layer-by-layer printing process result in highly accurate dental models and devices.
Challenges and Limitations
- Material Limitations
- Regulatory and Standardization Challenges
- Learning Curve
Material Limitations
Although 3D printing materials have improved over the years, there are still limitations in terms of biocompatibility, strength, and longevity. Researchers continue to work on developing materials that meet the stringent requirements of dental applications.
Regulatory and Standardization Challenges
The regulatory landscape for 3D-printed medical and dental devices is evolving and varies across regions. Standardization and clear guidelines are essential to ensure the safety and efficacy of 3D-printed dental products.
Learning Curve
Adopting and integrating 3D printing into dental practices require training and familiarization with the technology. Dentists and technicians need to invest time and effort to learn how to use 3D printers effectively.
Future Prospects
The future of 3D printing in dentistry looks promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at overcoming current limitations. Anticipated advancements include:
- Improved Materials
- Faster Printing Speeds
- Hybrid Printing
- Tele-Dentistry and Remote Printing
Improved Materials
Continued research to develop biocompatible and durable materials suitable for a wide range of dental applications.
Faster Printing Speeds
Technological advancements will likely lead to faster 3D printing processes, enhancing efficiency and productivity in dental labs.
Hybrid Printing
Integration of multiple materials and techniques, such as combining 3D printing with traditional manufacturing, to achieve optimal outcomes in dental device production.
Tele-Dentistry and Remote Printing
Utilizing 3D printing to fabricate dental devices remotely, enabling a more accessible and convenient approach to dental care, especially in remote or underserved areas.
Conclusion
3D printers and 3D printing technology have revolutionized dentistry, offering numerous advantages such as personalized treatment, increased efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced precision. Despite some challenges and limitations, ongoing research and advancements in materials and technology promise a bright future for 3D printing in dentistry. As the field continues to evolve, it is essential for dental professionals to stay updated with the latest developments and embrace this transformative technology to improve patient care and outcomes.