Taste is a vital sensory function that allows us to enjoy and discern different foods and beverages. It not only enhances the pleasure of eating but also plays a critical role in detecting potentially harmful substances. The sense of taste is a complex interplay between taste buds, sensory nerves, and the brain. However, several factors can disrupt this intricate process, leading to taste disorders. This article delves into the science of taste sensation, common problems associated with it, and potential solutions.

Table of Contents
ToggleThe Science of Taste Sensation
Taste, or gustation, is one of the five basic senses and is primarily detected by taste buds located on the tongue, soft palate, esophagus, and epiglottis.
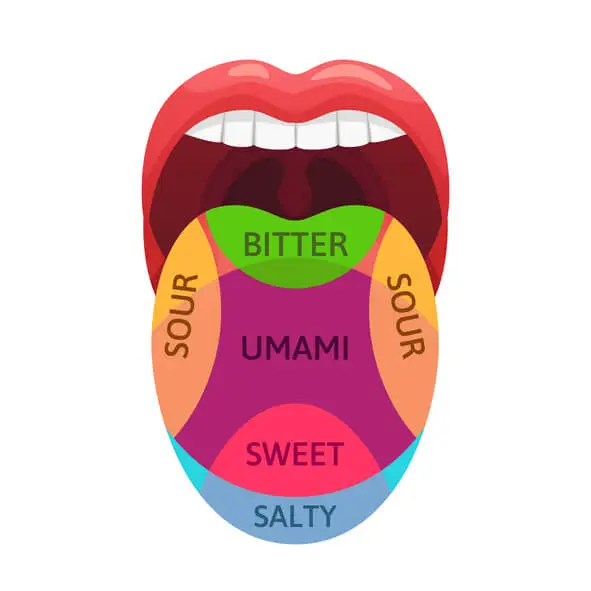
Human taste buds are responsible for detecting five primary taste qualities:
- sweet
- salty
- sour
- bitter
- umami
Sweet
Detected in response to sugars and certain proteins, the sweet taste signals energy-rich nutrients.
Salty
Activated by the presence of sodium ions, the salty taste helps maintain electrolyte balance.
Sour
Triggered by acids, the sour taste can indicate spoilage or fermentation.
Bitter
Often a signal of toxicity, the bitter taste is sensitive to a wide range of compounds.
Umami
A savory taste, umami is triggered by glutamate and nucleotides, indicating protein-rich foods.
Process of Taste Perception
The process of taste perception involves the following steps:
- Taste Buds and Receptors
- Signal Transduction
- Neural Pathways
- Brain Processing
Taste Buds and Receptors
Taste buds contain specialized receptor cells that bind to taste molecules. Each taste bud houses 50-150 receptor cells.
Signal Transduction
When a taste molecule binds to a receptor, it triggers a series of chemical reactions that generate an electrical signal.
Neural Pathways
This electrical signal travels via the gustatory nerves (facial nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, and vagus nerve) to the brainstem.
Brain Processing
The brainstem relays the signal to the thalamus, which then sends it to the gustatory cortex in the brain, where the taste is identified and perceived.
Common Taste Disorders
Taste disorders can significantly affect quality of life, leading to nutritional deficiencies, loss of appetite, and decreased enjoyment of food. Several conditions and factors can impair taste sensation:
- Ageusia
- Hypogeusia
- Dysgeusia
- Phantom Taste Perception
Ageusia
Complete loss of taste function, often resulting from damage to the gustatory system.
Hypogeusia
Reduced ability to taste, which may affect one or more of the primary taste modalities.
Dysgeusia
Distortion of taste perception, where ordinary tastes may be perceived as unpleasant or different from normal.
Phantom Taste Perception
Experiencing a taste sensation in the absence of any actual taste stimulus.
Causes of Taste Disorders
Taste disorders can arise from a variety of causes, including:
- Medical Conditions
- Medications
- Oral and Dental Issues
- Aging
Medical Conditions
- Infections
- Neurological Disorders
- Diabetes
- Cancer and Treatments
Infections
Upper respiratory infections, such as the common cold or flu, can temporarily impair taste sensation.
Neurological Disorders
Conditions like Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and multiple sclerosis can affect taste perception due to nerve damage.
Diabetes
Poorly controlled diabetes can damage nerves and blood vessels, leading to taste dysfunction.
Cancer and Treatments
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can damage taste buds and salivary glands, resulting in taste changes.
Medications
Certain medications, including antibiotics, antihistamines, and blood pressure drugs, can alter taste perception as a side effect.
Oral and Dental Issues
- Poor Oral Hygiene
- Dental Procedures
- Nutritional Deficiencies
Poor Oral Hygiene
Accumulation of plaque and tartar, as well as dental infections, can affect taste buds.
Dental Procedures
Dental treatments and surgeries can sometimes damage taste nerves.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Deficiencies in zinc, vitamin B12, and vitamin D can impair taste function.
Aging
Taste buds naturally decrease in number and sensitivity with age, leading to diminished taste perception.
Diagnosis of Taste Disorders
Diagnosing taste disorders involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and specific tests to evaluate taste function. Common diagnostic approaches include:
- Taste Strips and Solutions
- Electrogustometry
- Olfactory Testing
Taste Strips and Solutions
Patients are asked to identify different taste qualities using taste strips or solutions applied to the tongue.
Electrogustometry
This test uses small electrical currents to stimulate taste buds and measure their response.
Olfactory Testing
Since taste and smell are closely linked, olfactory testing may be conducted to rule out smell disorders.
Management and Treatment of Taste Disorders
The treatment of taste disorders depends on the underlying cause. Here are some approaches to managing taste dysfunction:
- Addressing Medical Conditions
- Medication Adjustment
- Nutritional Support
- Oral Hygiene and Dental Care
- Taste Training and Rehabilitation
Addressing Medical Conditions
Treating the underlying medical condition can often restore normal taste function. For example:
- Infections: Managing upper respiratory infections with appropriate medications can resolve temporary taste loss.
- Neurological Disorders: Medications and therapies to manage neurological conditions can help improve taste perception.
- Diabetes: Proper diabetes management, including blood sugar control, can mitigate taste dysfunction.
Medication Adjustment
If a medication is causing taste changes, a healthcare provider may adjust the dosage or switch to an alternative drug.
Nutritional Support
Correcting nutritional deficiencies through diet or supplements can improve taste sensation.
Oral Hygiene and Dental Care
Maintaining good oral hygiene and addressing dental issues can help restore taste function. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are essential.
Taste Training and Rehabilitation
Taste training programs, involving repeated exposure to different tastes, can help retrain the brain and improve taste perception in some cases.
Coping Strategies for Individuals with Taste Disorders
Living with a taste disorder can be challenging, but several coping strategies can help individuals manage their condition:
- Flavor Enhancement
- Texture Variation
- Small, Frequent Meals
- Hydration
- Consultation with a Dietitian
Flavor Enhancement
Using herbs, spices, and flavor enhancers can make food more palatable.
Texture Variation
Experimenting with different food textures can enhance the overall eating experience.
Small, Frequent Meals
Eating smaller, more frequent meals can make eating more manageable and enjoyable.
Hydration
Staying well-hydrated can help maintain taste bud function and prevent dry mouth.
Consultation with a Dietitian
Working with a dietitian can help develop a balanced and nutritious diet that accommodates taste changes.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Research into taste disorders is ongoing, with new insights and potential treatments emerging. Some promising areas of research include:
- Stem Cell Therapy
- Gene Therapy
- Pharmacological Interventions
- Neuroplasticity and Rehabilitation
Stem Cell Therapy
Investigating the potential of stem cells to regenerate damaged taste buds and nerves.
Gene Therapy
Exploring genetic approaches to correct taste dysfunction caused by inherited conditions.
Pharmacological Interventions
Developing drugs that can enhance or restore taste function by targeting specific pathways in the gustatory system.
Neuroplasticity and Rehabilitation
Understanding the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize itself, potentially leading to new rehabilitation techniques for taste disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the taste sensation?
Taste sensation, also known as gustatory perception, is the ability to detect and interpret different flavors through specialized sensory receptors called taste buds, located primarily on the tongue. These taste buds are sensitive to five primary tastes:
- Sweet – Often associated with sugar and carbohydrates, signaling energy-rich food.
- Sour – Typically detected in acidic substances like citrus fruits and fermented foods.
- Salty – Comes from sodium ions, which are crucial for maintaining electrolyte balance in the body.
- Bitter – Often associated with toxic or unripe foods, helping as a natural defense mechanism.
- Umami – A savory taste linked to glutamate, commonly found in meats, cheese, and broths.
These taste sensations work together with smell, texture, and temperature to create the full perception of flavor.
What is a synonym for taste sensation?
A synonym for taste sensation is gustatory perception or flavor perception. Other related terms include palate perception, flavor detection, and taste recognition.
Which nerve carries taste sensation?
Taste sensations are transmitted to the brain via three major cranial nerves:
- Facial nerve (Cranial Nerve VII) – Carries taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (Cranial Nerve IX) – Transmits taste from the posterior one-third of the tongue.
- Vagus nerve (Cranial Nerve X) – Conveys taste sensations from areas like the epiglottis and soft palate.
These nerves send taste signals to the gustatory cortex in the brain, where the perception of flavor is processed.
Is taste a chemical sensation?
Yes, taste is classified as a chemical sensation because it relies on the interaction of chemical compounds in food with taste receptors on the tongue. When food molecules dissolve in saliva, they bind to specific receptors on the taste buds, triggering electrical signals that the brain interprets as different tastes. This is distinct from mechanical sensations (such as touch) and thermal sensations (such as temperature perception).
What is the disorder of taste sensation?
Disorders affecting taste sensation include:
- Dysgeusia – A distorted taste perception, where foods may taste metallic, bitter, or foul.
- Ageusia – A complete loss of taste sensation.
- Hypogeusia – A reduced ability to taste certain flavors.
- Parageusia – An abnormal taste perception that can be persistent or occur temporarily.
- Phantogeusia – The sensation of taste without any external stimuli (often linked to nerve damage).
These conditions may result from infections (e.g., COVID-19), nerve damage, medication side effects, or underlying health issues like diabetes and neurological disorders.
How to check taste sensation?
Taste sensation can be tested through a gustatory test, which involves:
- Applying solutions of sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami to different areas of the tongue to assess taste function.
- Using taste strips containing various flavors.
- Performing a “sip, swish, and swallow” test with flavored liquids.
- Medical professionals may also use electrogustometry, which applies a mild electrical current to the tongue to stimulate taste perception.
If someone experiences changes in their taste, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.
Is taste really 80% smell?
Yes, about 80% of what we perceive as taste actually comes from olfaction (smell) rather than taste alone. This is why food seems flavorless when you have a stuffy nose. The nasal cavity and olfactory receptors detect volatile molecules from food, sending signals to the brain that combine with taste perception to create the full flavor experience.
This interaction is called retro-nasal olfaction, where scents from food travel to the olfactory receptors as we chew and swallow. This explains why wine tasting, coffee appreciation, and complex dishes rely heavily on aroma.
What is it called when you can taste feelings?
The ability to experience tastes in response to emotions, words, or sounds is called lexical-gustatory synesthesia. This rare neurological phenomenon causes individuals to associate certain words, emotions, or music with specific taste sensations.
For example, a person with synesthesia might experience a sweet or sour taste when hearing a particular name or feel a metallic taste when experiencing strong emotions like fear or excitement. This condition is believed to result from cross-wiring in the brain’s sensory processing centers.
What is a weird sense of taste?
A “weird” sense of taste can refer to unusual or distorted taste perceptions, often due to medical conditions or sensory misinterpretations. Some examples include:
- Parageusia – An abnormal taste that is persistent or occurs suddenly, such as a metallic or foul taste.
- Taste hallucinations (Phantogeusia) – The sensation of taste when no food or drink is present.
- Hypergeusia – An enhanced sensitivity to taste, making flavors feel overly intense.
- Dysgeusia – A persistent bad taste (such as metallic or bitter) in the mouth, which can result from medications, chemotherapy, or nerve damage.
If a person experiences a strange or distorted sense of taste for an extended period, it is best to seek medical advice to rule out underlying conditions.
Conclusion
Taste sensation is a complex and essential function that contributes significantly to our quality of life. While taste disorders can be distressing and challenging to manage, understanding their causes and potential treatments can help individuals and healthcare providers address these issues effectively. Advances in medical research and emerging therapies offer hope for improved diagnosis and treatment of taste dysfunction in the future. By raising awareness and promoting further research, we can enhance the lives of those affected by taste disorders and continue to enjoy the rich and diverse world of flavors.

