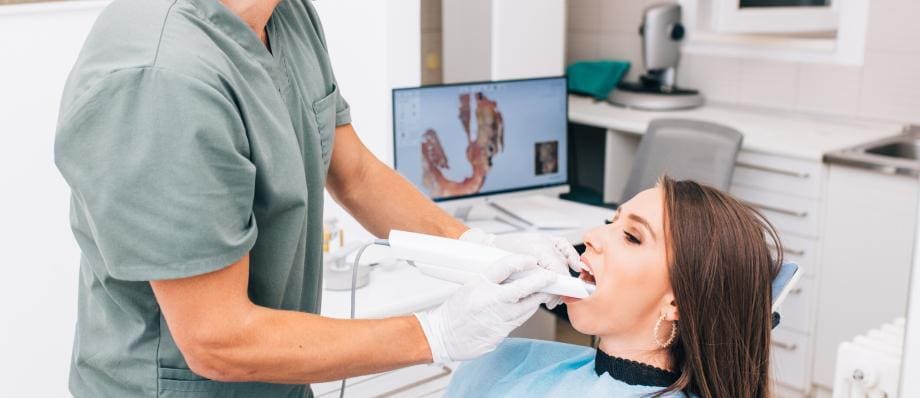
The field of dentistry has witnessed remarkable advancements in technology, transforming the way oral healthcare is delivered. One such innovation is dental digital scanner, which have revolutionized the traditional dental impression process.
These cutting-edge devices capture highly accurate digital impressions of patients’ teeth and oral structures, replacing the need for messy and uncomfortable conventional impressions. In this article, we will explore the benefits, working principles, applications, and future potential of dental digital scanner.
Table of Contents
ToggleAdvantages of Dental Digital Scanner
Dental digital scanners offer numerous advantages over traditional impression techniques:
- Convenience
- Accuracy
- Real-time visualization
Convenience
They eliminate the discomfort and inconvenience associated with conventional impressions. Patients no longer need to endure the unpleasant taste and texture of impression materials or the discomfort of trays placed in their mouths.
Accuracy
Digital scanner provides greater accuracy and precision. It captures detailed 3D images of the teeth and oral structures, ensuring a more accurate representation for the fabrication of dental restorations. This enhanced accuracy minimizes the need for retakes, reducing chair time and improving overall patient satisfaction.
Real-time visualization
scanners enable real-time visualization of the digital impressions on a computer screen. Dentists can immediately assess the quality of the scan and make any necessary adjustments before sending the data to the dental laboratory, improving communication and collaboration between the dentist and the lab technician.
How Dental Digital Scanner Works
Dental digital scanner utilizes state-of-the-art technology to capture digital impressions. The scanners employ either an optical or laser based system to record the topographical data of the patient’s teeth and surrounding tissues. These scanners consist of a handheld wand-like device that is moved over the patient’s oral structures to capture the data.
Optical scanners utilize a series of cameras and optical sensors to record the surface details. These scanners emit a light source onto the teeth and use cameras to capture images of the reflected light. The data collected is then processed using advanced algorithms to create a digital model.
On the other hand, laser scanners employ a laser beam that sweeps over the teeth, measuring the distances between the scanner and the tooth surface. The reflected laser light is collected and analyzed to create a virtual 3D model.
Both types of scanners rely on software that stitches together multiple images or point clouds to create a comprehensive digital impression. The resulting digital model can be stored electronically, shared with dental laboratories, and used for a range of applications, including the design and fabrication of dental restorations, orthodontic aligners, and appliances.
Applications of Dental Digital Scanner
Dental digital scanners have broad applications in various areas of dentistry.
- Restorative dentistry
- Orthodontic treatments
- Dental implant
- Prosthodontics
Restorative dentistry
One of the primary applications is in restorative dentistry, where digital impressions are used to create crowns, bridges, inlays and onlays, and dental laminates. The accurate digital models obtained from scanners enable the fabrication of precisely fitting restorations, resulting in improved patient outcomes.
Orthodontic treatments
Orthodontics is another field that greatly benefits from digital scanner. Orthodontists use digital impressions to create customized clear aligners, such as Invisalign, for patients seeking orthodontic treatment. The digital models provide a precise representation of the patient’s teeth and facilitate the planning and monitoring of tooth movements throughout the treatment process.
Dental implant
Digital scanners find applications in implant dentistry. They aid in the planning and placement of dental implants by creating virtual models that allow dentists to evaluate bone quality, plan implant position, and design custom surgical guides for precise implant placement.
Prosthodontics
Additionally, dental digital scanner contributes to the field of prosthodontics, enabling the creation of digital dentures and removable partial dentures. The digital impressions captured by the scanners simplify the design and fabrication processes, resulting in more comfortable and accurately fitting prosthes.
Conclusion
Dental digital scanners have undeniably revolutionized the field of dentistry by replacing traditional impression techniques with advanced digital technology. These scanners offer numerous benefits, including improved patient comfort, enhanced accuracy, and real-time visualization of digital impressions. With applications ranging from restorative dentistry to orthodontics and implantology, dental digital scanners have become indispensable tools for modern dental practices.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in digital scanning, such as improved scanning speed, increased portability, and integration with other digital systems. The future of dentistry is undoubtedly digital, with dental digital scanner leading the way towards more efficient, accurate, and patient-centered oral healthcare.