Antioxidants are naturally occurring or synthetic substances that help prevent or slow down oxidative damage in the body. They play a crucial role in neutralizing harmful molecules called free radicals, which are linked to aging, chronic diseases, and overall cellular damage. In this article, we will explore the significance of antioxidants, their sources, health benefits, and how they impact various bodily functions.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are Antioxidants?
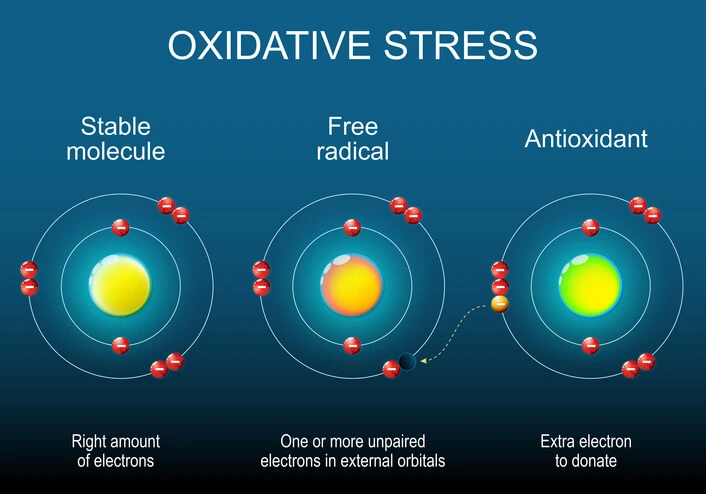
Antioxidants are molecules that combat oxidative stress caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells by stealing electrons from other molecules, leading to cellular dysfunction. While the body naturally produces free radicals through metabolic processes, external factors like pollution, radiation, smoking, and unhealthy diets can increase their levels, leading to accelerated aging and disease.
The body has its own defense mechanisms, including enzymes and naturally occurring antioxidants, but external sources of antioxidants from food and supplements enhance this protective system.
Types of Antioxidants
There are several types of antioxidants, categorized based on their function and origin:
- Endogenous Antioxidants
- Exogenous Antioxidants
Endogenous Antioxidants
These are produced by the body and include:
- Superoxide dismutase (SOD)
- Glutathione
- Catalase
- Coenzyme Q10
Exogenous Antioxidants
These come from external sources such as food and supplements and include:
- Vitamin C – Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers
- Vitamin E – Found in nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables
- Beta-carotene – Found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and pumpkins
- Polyphenols – Found in green tea, red wine, and berries
- Flavonoids – Found in dark chocolate, apples, and onions
How Antioxidants Work
Antioxidants neutralize free radicals by donating an electron without becoming unstable themselves. This process helps prevent the chain reaction of oxidative damage that contributes to aging and chronic diseases. Additionally, antioxidants support cellular repair mechanisms and strengthen the immune system.
Health Benefits of Antioxidants
Antioxidants are linked to numerous health benefits, making them a crucial component of a balanced diet. Here are some of the primary benefits:
- Anti-Aging and Skin Health
- Supports Heart Health
- Boosts Brain Function and Reduces Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Strengthens the Immune System
- Cancer Prevention
- Aids in Eye Health
- Improves Respiratory Health
Anti-Aging and Skin Health
Oxidative stress contributes to skin aging by damaging collagen and elastin, leading to wrinkles and loss of elasticity. Antioxidants such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and polyphenols help reduce skin damage caused by UV exposure and pollution, keeping the skin youthful and radiant.
Supports Heart Health
Heart disease is one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide. Antioxidants like flavonoids, vitamin C, and vitamin E help reduce inflammation, lower blood pressure, and prevent the oxidation of LDL cholesterol, which is a major contributor to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
Boosts Brain Function and Reduces Neurodegenerative Diseases
Antioxidants play a significant role in brain health by protecting neurons from oxidative damage. Studies suggest that diets rich in antioxidants may lower the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Polyphenols from berries, green tea, and dark chocolate have been shown to enhance cognitive function and memory.
Strengthens the Immune System
A strong immune system is essential for fighting infections and diseases. Antioxidants like vitamin C and zinc help enhance immune function by reducing inflammation and supporting white blood cell activity. They also aid in faster recovery from illnesses.
Cancer Prevention
Free radicals have been linked to DNA damage, which can lead to cancer development. Antioxidants help prevent cellular mutations and inhibit the growth of cancer cells. While no single antioxidant can completely prevent cancer, consuming a variety of antioxidant-rich foods can significantly reduce the risk.
Aids in Eye Health
Macular degeneration and cataracts are common age-related eye disorders. Antioxidants such as lutein and zeaxanthin, found in leafy greens, protect the eyes from oxidative damage caused by UV rays and blue light from digital screens.
Improves Respiratory Health
Exposure to pollutants and smoking leads to oxidative damage in the lungs, increasing the risk of respiratory diseases like asthma and COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease). Antioxidants help reduce inflammation in the lungs and improve overall respiratory function.
Best Sources of Antioxidants
To maintain optimal health, it is essential to consume a variety of antioxidant-rich foods. Some of the best sources include:
- Fruits – Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries), citrus fruits, grapes, and apples.
- Vegetables – Spinach, kale, carrots, sweet potatoes, and bell peppers.
- Nuts and Seeds – Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and sunflower seeds.
- Beverages – Green tea, red wine, and coffee.
- Herbs and Spices – Turmeric, cinnamon, ginger, and oregano.
- Dark Chocolate – Contains flavonoids that promote heart and brain health.
Antioxidant Supplements: Are They Necessary?
While a diet rich in antioxidants is the best way to obtain them, supplements can be beneficial in some cases. However, excessive intake of synthetic antioxidants can have adverse effects, such as interfering with natural bodily processes and increasing the risk of certain diseases.
Studies suggest that high doses of antioxidant supplements, such as beta-carotene and vitamin E, may not provide the same benefits as naturally occurring antioxidants from food. It is always best to consult a healthcare provider before taking antioxidant supplements.
The Role of Antioxidants in Exercise Recovery
Exercise-induced oxidative stress can cause muscle fatigue and soreness. Consuming antioxidant-rich foods post-workout helps in muscle recovery and reduces inflammation. However, excessive antioxidants may blunt the beneficial effects of exercise by interfering with natural adaptation processes.
Potential Risks of Excess Antioxidants
While antioxidants are beneficial, excessive intake can be harmful. High doses of certain antioxidants, such as vitamin A and vitamin E, have been linked to increased risks of mortality, liver toxicity, and interference with chemotherapy treatments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can antioxidants help with weight loss?
While antioxidants do not directly cause weight loss, they support metabolism and reduce inflammation, which can contribute to better weight management.
What is the best way to get antioxidants?
The best way to obtain antioxidants is through a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains rather than relying on supplements.
Are antioxidant supplements safe?
Antioxidant supplements can be beneficial in moderation, but excessive intake may have adverse effects. It is best to consult a healthcare provider before use.
Can antioxidants prevent cancer?
Antioxidants help reduce the risk of cancer by preventing cellular damage, but they do not guarantee complete prevention.
Do cooking methods affect antioxidant levels in food?
Yes, cooking methods like boiling and frying can reduce antioxidant levels in food. Steaming and raw consumption help retain the most nutrients.